Figure 1: A human-in-the-loop approach enables scalable, pixel-level annotation of large image collections.
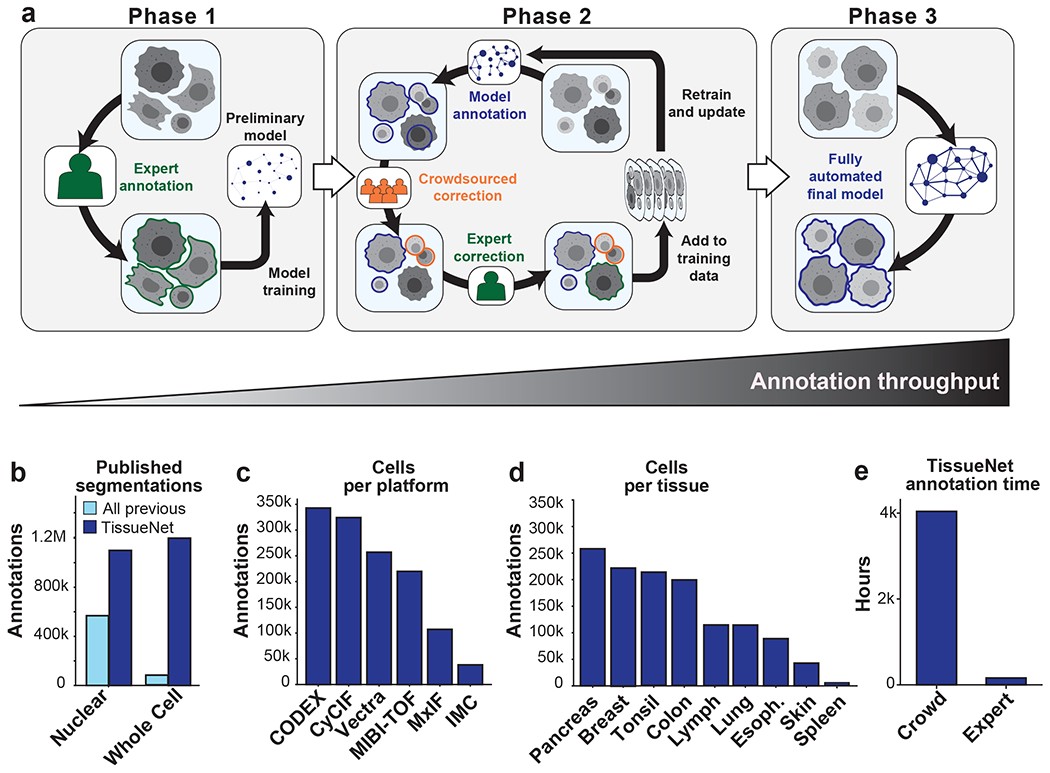
a, This approach has three phases. During phase 1, annotations are created from scratch to train a model. During phase 2, new data are fed through a preliminary model to generate predictions. These predictions are used as a starting point for correction by annotators. As more images are corrected, the model improves, which decreases the number of errors, increasing the speed with which new data can be annotated. During phase 3, an accurate model is run without human correction. b, TissueNet has more nuclear and whole-cell annotations than all previously published datasets. c, The number of cell annotations per imaging platform in TissueNet. d, The number of cell annotations per tissue type in TissueNet. e, The number of hours of annotation time required to create TissueNet.
