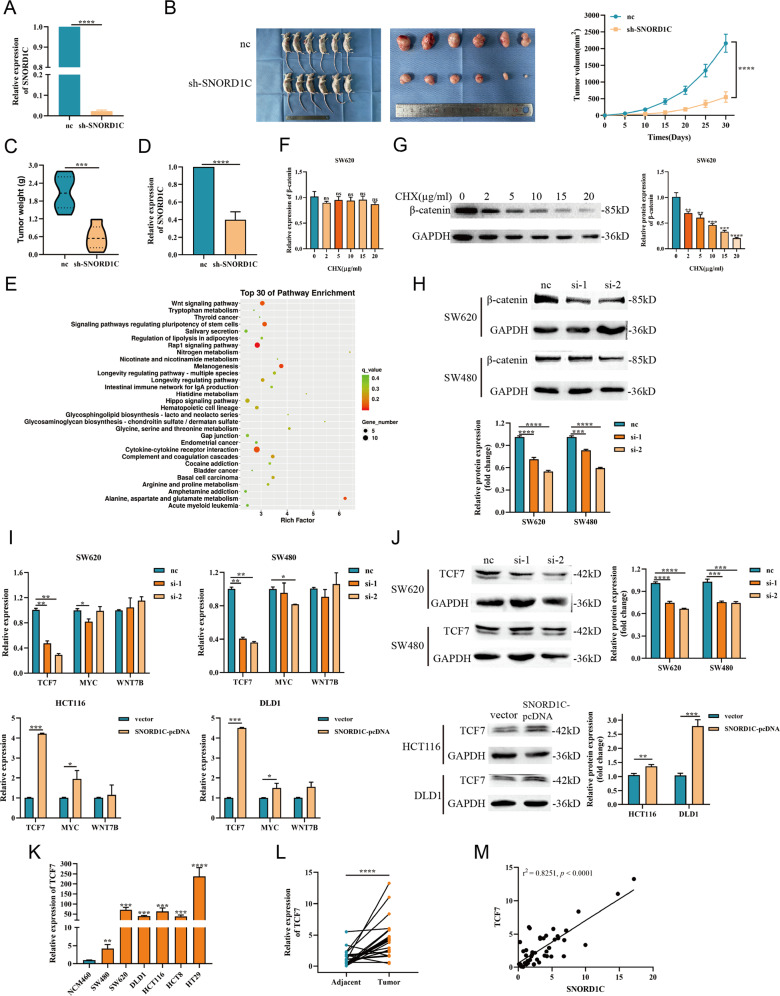
Fig. 4. SNORD1C altered the carcinogenesis of CRC cells in vivo, and knocking down SNORD1C inhibited activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
A qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of SNORD1C after lentiviral infection with nc and sh-SNORD1C. B Representative images of tumors in nude mice xenograft tumor models and tumor growth curves between nc and sh-SNORD1C groups. C, D Comparison of tumor weight and qRT-PCR analysis of SNORD1C expression in the model mice. E KEGG analysis of differentially expressed genes after SNORD1C knockdown. The top 30 pathways are shown. F The mRNA expression of β-catenin showed no difference with the increase of CHX concentration. G The protein expression of β-catenin decreased with the increase of CHX concentration. H Western blotting experiments were performed to determine β-catenin expression in SNORD1C-knockdown SW620 and SW480 cells. I qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of Wnt pathway-related genes in SNORD1C-knockdown cells. J Western blotting was used to evaluate TCF7 levels in SNORD1C-knockdown cells. K, L qRT-PCR was used to detect TCF7 levels in CRC cell lines and paired tissue samples. M Correlation analysis between SNORD1C and TCF7 expression in paired tissue samples. CHX, cycloheximide, the translational inhibitor.