Fig. 2.
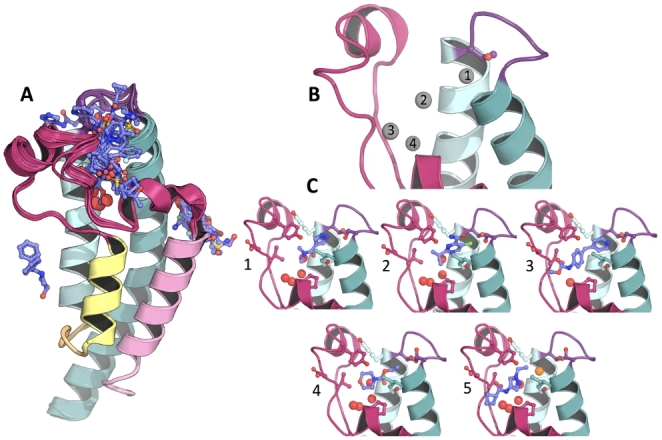
Overview of the fragment hits against the C2 crystal form. (A) Overlay of all structures resulting from the crystallographic high-throughput screening. The Kac binding is the most populated site. The other sites can be seen on the right and left of the Kac binding site. An additional fragment hit is located behind the purple BC-loop. (B) illustrates the 4 fragment binding subsites with the B1, B2, B3 and B4 denotating the BC-interface, central void, ZA-channel and the water cavity, respectively, as grey spheres. (C) shows selected fragment binding poses to illustrate the diverse types of interactions and binding regions identified from the results. C1 shows F421 (PDB: 5RK9) that forms an H-bond with SER1392 at the BC-interface. C2 shows F126 (PDB: 5RKE) that forms a halogen bond with THR1396 and SER1401 at the BC-interface. C3 shows F558 (PDB: 5RJV) which has 2 aromatic 6 membered rings that both form perpendicular pi-stacking with TYR1350 and TYR1395. C4 shows F393 (PDB: 5RK7) which has a morpholine moiety that fills the central void. Finally, C5 shows F368 (PDB: 5RKN) which forms H-bonds on the ZA-channel with backbone nitrogen and oxygen of ASP1346 and PRO1350, respectively
