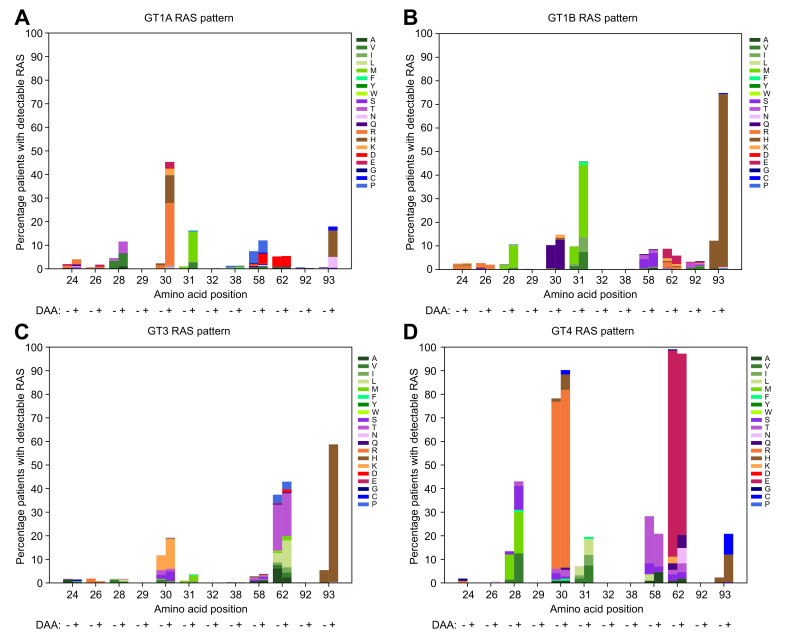
Fig. 3.
NS5A resistance patterns in different genotypes.
NS5A amino acid sequences obtained from patients treated with NS5A inhibitor-containing regimens before (DAA: -) and after (DAA: +) treatment were grouped according to their genotypes. The number of sequences before/after DAA treatment was 697/424 in GT1a, 262/451 in GT1b, 479/497 in GT3, 108/108 in GT4. The number of variant amino acids relative to the reference at each indicated position was enumerated and normalized to the total number of sequences in the respective genotypes. The amino acids are colored according to their side-chain biochemical properties: green = hydrophobic, purple = polar uncharged, orange = positively charged, red = negative charged, blue = special cases. The percentages of patients with detectable RASs in genotypes 1a, 1b, 3, and 4 are shown. The NS5AI-naïve sequences contained subtypes 3a/b/g/h and 4a/d/f/l/o/q/r/v. The NS5AI-exposed sequences contained subtypes 3a/b/g/h/k and 4a/b/d/f/g/k/n/o/q/r/v. DAA, direct-acting antiviral; GT, genotype; RASs, resistance-associated substitutions.