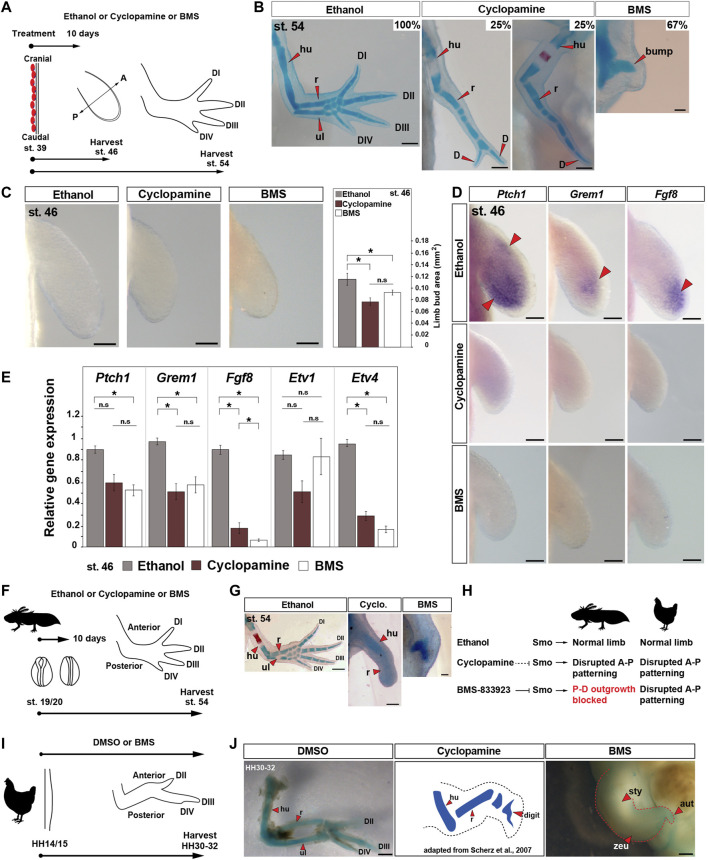
FIGURE 1.
Small-molecule smoothened antagonist BMS-833923 inhibits limb bud outgrowth in axolotl larvae. (A) Design for ethanol (control), cyclopamine, and BMS treatments in axolotl. Limbs are aligned with anterior “A” on the top and posterior “P” on the bottom. Red ovals depict dorsal muscle blocks. (B) Representative images of Alcian blue/Alizarin red–stained ethanol-, cyclopamine-, or BMS-treated stage 54 limbs (limb n = 30 for ethanol, 24 for cyclopamine, and 36 for BMS-833923). Scale bar = 500 µm. (C) Limb bud area measurements in ethanol (control)-, cyclopamine-, or BMS-treated limbs [one-way ANOVA, Tukey–Kramer HSD post hoc test, F = 8.628; Tukey–Kramer HSD post hoc test, p = 0.0026 (ethanol vs. cyclopamine), p = 0.046 (ethanol vs. BMS), and p = 0.34 (cyclopamine vs. BMS); n = 6 per treatment]. Scale bar = 100 µm. (D) In situ hybridization for genes Ptch1, Grem1, and Fgf8 in ethanol-, cyclopamine-, or BMS-treated stage 46 limbs (n = 3 or 4 per gene). Red arrows: expression domain. Scale bar = 100 µm. (E) qRT-PCR for Ptch1, Grem1, Fgf8, Etv1, and Etv4 expression in stage 46 limbs post ethanol, cyclopamine, or BMS treatments [one-way ANOVA, Tukey–Kramer HSD post hoc test; Ptch1: F = 7.98, p = 0.06 (ethanol vs. cyclopamine), p = 0.02 (ethanol vs. BMS), and p = 0.65 (cyclopamine vs. BMS); Grem1: F = 8.65, p = 0.018 (ethanol vs. cyclopamine), p = 0.048 (ethanol vs. BMS), and p = 0.68 (cyclopamine vs. BMS); Fgf8: F = 301.43, p < 0.0001 (ethanol vs. cyclopamine), p < 0.0001 (ethanol vs. BMS), and p = 0.03 (cyclopamine vs. BMS); Etv1: F = 2.986, p = 0.16 (ethanol vs. cyclopamine), p = 0.99 (ethanol vs. BMS), and p = 0.17 (cyclopamine vs. BMS); Etv4: F = 225.92, p < 0.0001 (ethanol vs. cyclopamine), p < 0.0001 (ethanol vs. BMS), and p = 0.13 (cyclopamine vs. BMS); n = 3 per treatment]. (F) Design for ethanol, cyclopamine, or BMS treatments at neural fold stage 19/20 in axolotls. (G) Alcian blue/Alizarin red staining at stage 54 for neural fold treatments with ethanol, cyclopamine, or BMS (n = 3 per treatment). Scale bar = 500 µm. (H) Schematic depicting the mode of actions of ethanol, cyclopamine, and BMS in axolotl and chick limb buds. (I) Design for ethanol, cyclopamine, or BMS treatments at HH14/15 in chick embryos. (J) Alcian blue/Alizarin red–stained DMSO, and cyclopamine-treated (adapted from the work of Scherz et al., 2007) and BMS-treated limbs at HH30-32 (n = 4 per treatment). Scale bar = 1 mm. Error bars: SEM; and asterisk: significant p-values. hu, humerus; r, radius; ul, ulna; D, digit; sty, stylopod; zeu, zeugopod; and aut, autopod.