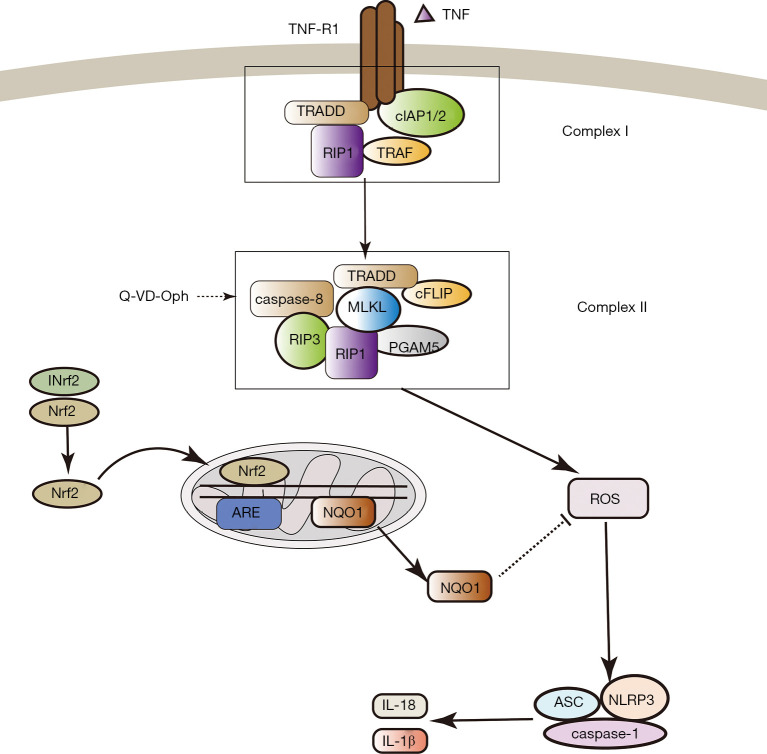
Figure 5.
Nrf2 negatively regulated NLRP3 inflammasome activity in necroptosis in a ROS-dependent manner. TNF-alpha was significantly promoted after cerebral ischemia; TNF-alpha combined with TNFR1 and recruited a series of proteins to form complex I (TRADD, RIP1, TRAF2, TRAF5, cIAP1, cIAP2, and ubiquitin enzyme complex). TNFR1 was dissociated from complex I and form complex II (RIP1, RIP3, TRADD, FADD and caspase-8). In complex II, if RIP1 and RIP3 are inactivated by proteolytic cleavage by caspase-8, apoptosis was induced; however, with apoptosis inhibitor (Q-VD-OPh), caspase-8 was inhibited, the RIP1 kinase combines with RIP3 to form necrosome. Necroptosis leading to release of DAMPs are believed to participate in triggering inflammatory processes, which can initiate activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. In this experiment, we proved that Nrf2/ NQO1 can further inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome through ROS dependent way. Nrf2, nuclear factor E2-related factor-2; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; NQO1, NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1; TRADD, Fas-associated death domain; TRAF2, Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor associated factor 2; TRAF5, Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor associated factor 5; cIAP1, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1; cIAP2, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 2; RIP1, receptor interacting protein kinase 1; RIP3, receptor interacting protein kinase 3; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns.