FIGURE 4.
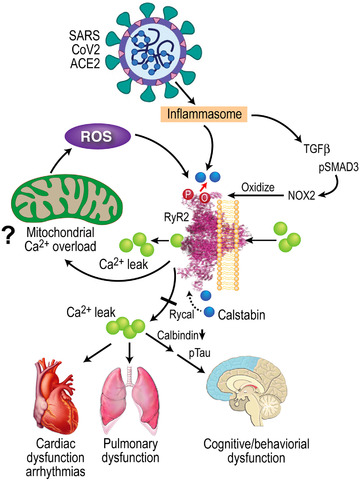
SARS‐CoV‐2 infection results in leaky ryanodine receptor 2 (RyR2) that may contribute to cardiac, pulmonary, and cognitive dysfunction. SARS‐CoV‐2 infection targets cells via the angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, inducing inflammasome stress response/activation of stress signaling pathways. This results in increased transforming growth factor‐β (TGF‐β) signaling, which activates SMAD3 (pSMAD) and increases NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2) expression and the amount of NOX2 associated with RyR2. Increased NOX2 activity at RyR2 oxidizes the channel, causing calstabin2 depletion from the channel macromolecular complex, destabilization of the closed state, and ER/SR calcium leak that is known to contribute to cardiac dysfunction, 55 arrhythmias, 61 pulmonary insufficiency, 23 , 25 and cognitive and behavioral abnormalities associated with neurodegenreation. 24 , 26 Decreased calbindin in COVID‐19 may render brain more susceptible to tau pathology. Rycal drugs fix the RyR2 channel leak by restoring calstabin2 binding and stabilizing the channel closed state. Fixing leaky RyR2 may improve cardiac, pulmonary, and cognitive function in COVID‐19.
