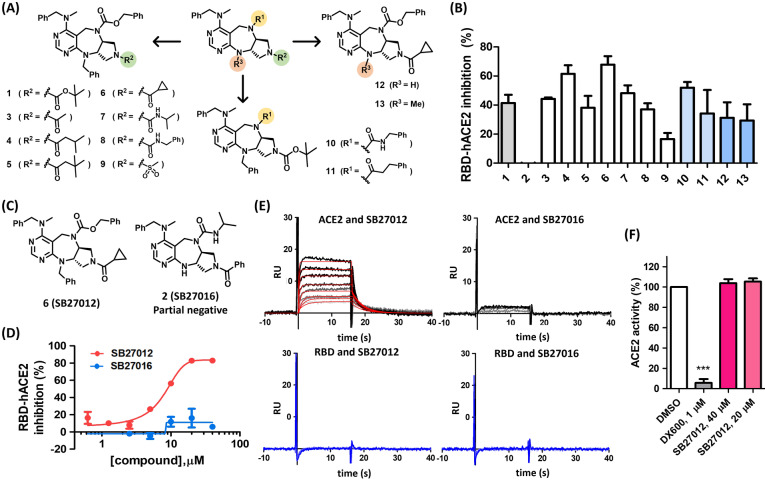
Figure 2.
Small‐molecule inhibitors of RBD–ACE2 interaction bind ACE2 without affecting ACE2 enzymatic activity. A) Compounds synthesized for the structure–activity relationship study. B) RBD–ACE2 sandwich ELISA assay data presented as % inhibition using compounds shown in (A) at 20 μM, n=2. C) Chemical structures of active compound 6 (SB27012) and partial negative compound 2 (SB27016). D) RBD–ACE2 ELISA assay, dose‐response experiments for SB27012 and SB271016; IC50 for SB27012 is 7.7±0.5 μM. E) Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis of immobilized ACE2 and RBD, representative SPR data, SB27012 (0.156–5 μM) and SB27016 (0.625–5 μM), n=3. Kinetic constants for SB27012 with immobilized ACE2: for association (k a) (7.5±4.8)×105 M−1 s−1, for dissociation (k d) (9.9±4.1)×10−2 s−1, for binding affinity (K d) (2.1±0.6)×10−7 M. F) ACE2 enzymatic assay data presented as % activity, n=3.