Figure 1.
Ad26.COV2.S vaccine protects 129S2 mice against challenge with WA1/2020 N501Y/D614G and B.1.621
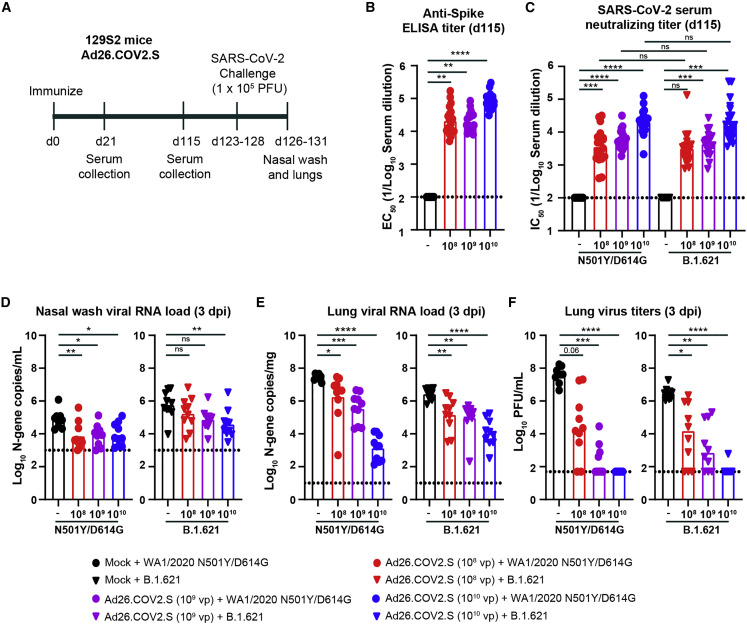
(A) Experimental setup.
(B) Serum anti-S protein antibody response (EC50) in control mice (black symbols) and mice immunized with 108 (red symbols), 109 (purple symbols), or 1010 (blue symbols) of Ad26.COV2.S (∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 by non-parametric one-way ANOVA with a Dunn’s post-test).
(C) Serum neutralizing titer (IC50) against WA1/2020 N501Y/D614G (circles) or B.1.621 (triangles) measured by FRNT from 129S2 mice immunized once with 108 (red symbols), 109 (purple symbols), or 1010 (blue symbols) of Ad26.COV2.S (∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ns = not significant by non-parametric one-way ANOVA with a Dunn’s post-test).
(D–F) 129S2 mice were challenged with 105 PFU of the WA1/2020 N501Y/D614G (circles) or B.1.621 (triangles) variant of SARS-CoV-2, and nasal washes (D) and lungs (E and F) were collected for analysis of viral RNA levels by qRT-PCR (D) and infectious virus by plaque assay (E and F) (∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗p < 0.05, ns = not significant by one-way ANOVA with a Dunnett’s [D and E] or Dunn’s [F] post-test).
(B–F) Bars indicate the geometric mean values, and dotted lines are the limits of detection (LODs) of the assays. Animals at the limit of detection are arbitrarily assigned this value. These values are combined with those having values above the limit to determine the GMT. The results are from two independent experiments, and each symbol represents an individual animal.
See also Figure S1.