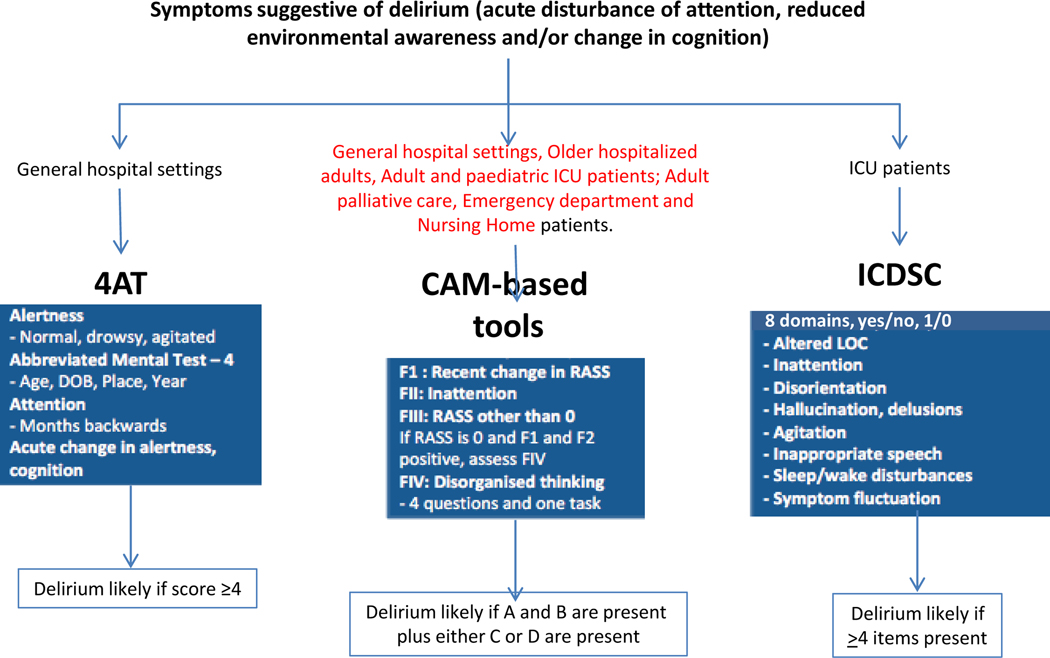
Figure 5. Common tools to screen for delirium in different settings.
Once there is suspicion of delirium based on the presence of symptoms such as acute disturbance of attention, reduced environmental awareness and/or changes in cognition, the choice of screening tool is made based on the setting. The 4 A’s test (4AT) is a 4-item test used in general hospital settings. A score ≥4 indicates delirium is likely. Confusion assessment method (CAM)-based tools, such as the CAM, CAM-ICU, brief-CAM, paediatric-CAM and preschool-CAM, assess four features, Features A–D (or Features 1–4 depending on the specific tool). For delirium to be present according to CAM based tools, A and B must be present, plus either C or D. The Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist (ICDSC) is a delirium assessment tool measuring 8 domains, recorded as yes (present; score 1) or no (absent; score 0) answers. Delirium is likely for a score ≥4. The clinical tools described, except for ICDSC, are snapshot assessments. *depending on the tool used, Features A–D may be called 1–4 and will be assessed in different ways. DOB, date of birth; LOC, level of consciousness.