Figure 4 |. RAPTR enables facile antigen identification for T cell receptors.
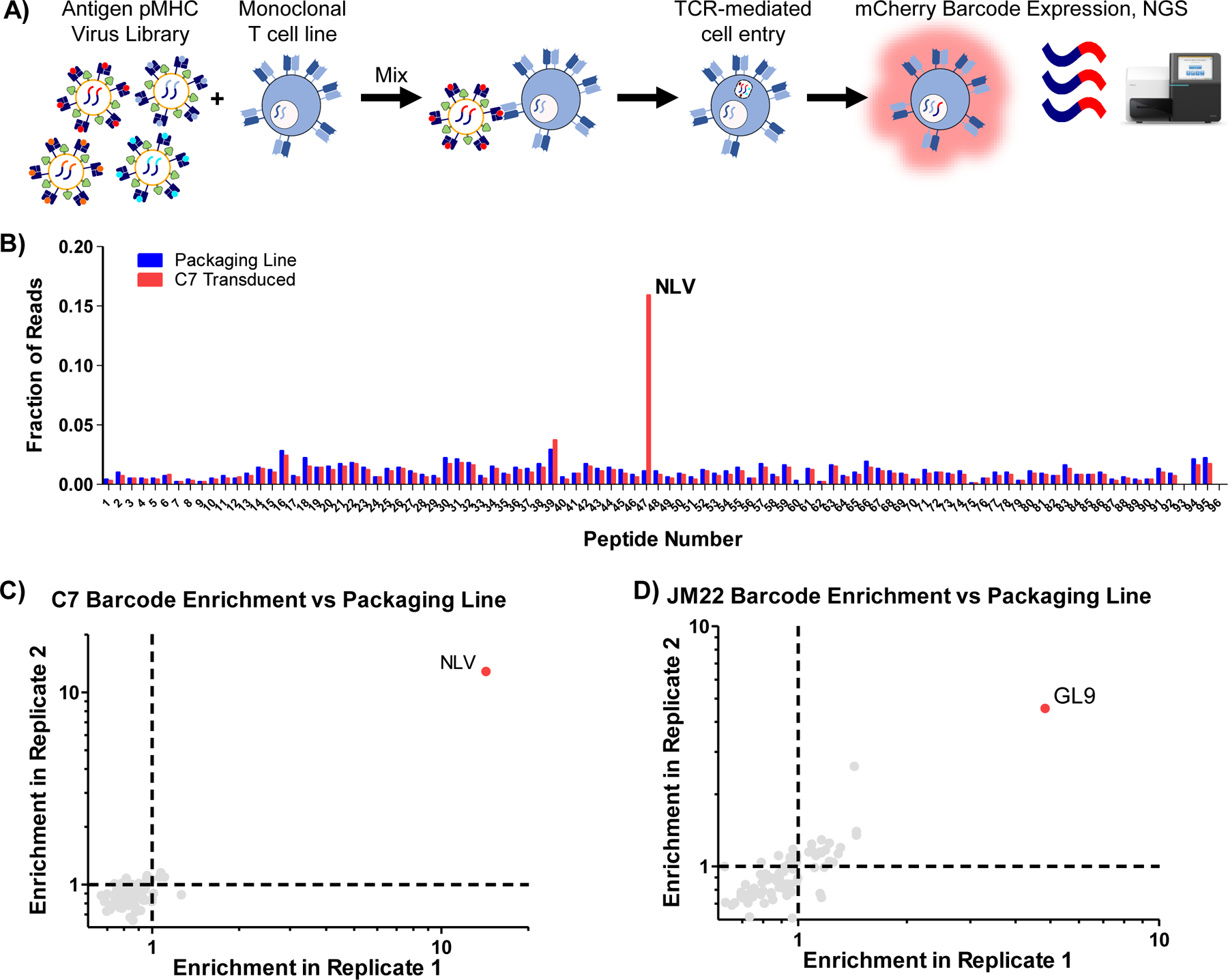
A, Workflow for RAPTR on monoclonal cell lines. The 96-member pMHC-displaying lentiviral library was mixed with J76 cells expressing a known TCR. After 2 days of infection, genomic DNA from unsorted transduced cells was harvested and analyzed by NGS. B, Read fraction of barcodes following infection of C7 TCR-transduced J76 cells. Blue bars represent the read fractions of barcodes from the 293T packaging cell line used to produce the viral library, and provides the unenriched (null) distribution absent TCR selection. The red bars indicate the read fraction in transduced C7-expressing J76 cells, revealing the selectivity of the TCR based on increasing read fraction of the barcode for the cognate ligand (NLV). C, Comparison of antigen enrichment relative to the packaging line upon library infection of C7 TCR-transduced J76 cells across two additional replicates. D, Comparison of antigen enrichment relative to the packaging line upon library infection of JM22 TCR-transduced J76 cells across two replicates.
