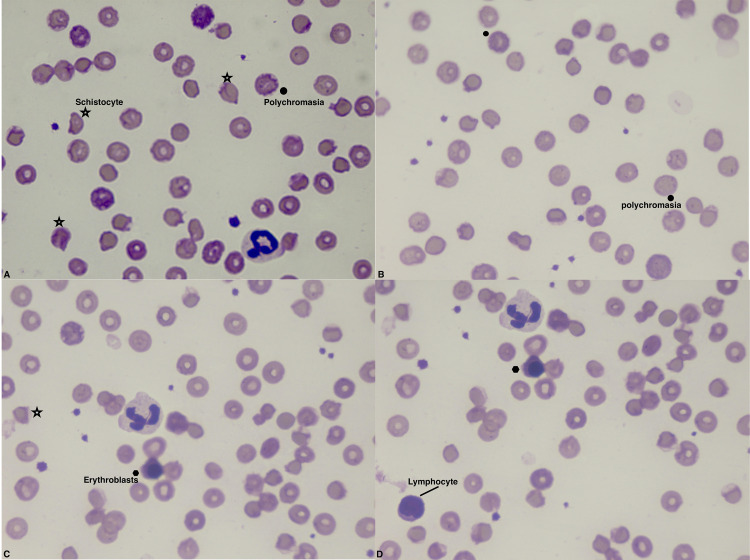
Figure 1. Peripheral blood smear at admission.
The smear was stained with May–Grünwald–Giemsa solution. There is marked anisocytosis and poikilocytosis, which is unspecific. Polychromasia is present, which is typically observed in blood disorders that result in the premature release of RBCs from the bone marrow. Schistocytes (RBC fragments indicating hemolysis) are also present. Erythroblasts with off-center nuclei containing dense chromatin can be seen; these are typical of severe anemia and a characteristic finding of hemolytic disease. Neutrophil hypersegmentation is visible in panels A, C, and D, and lymphocyte is present in panel D. Star = schistocyte, black dot = polychromasia.