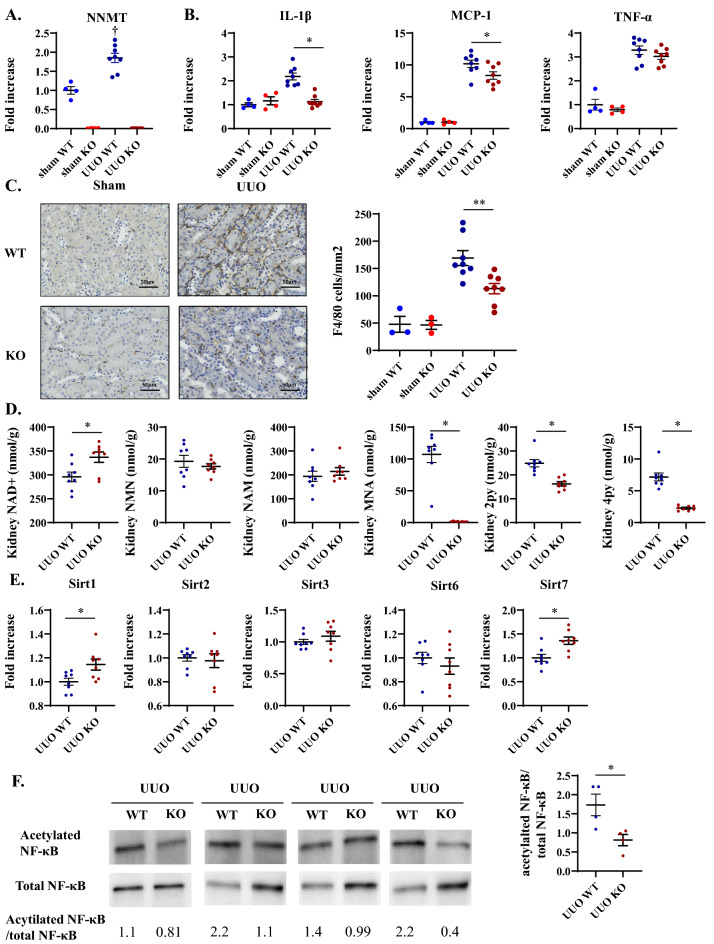
Figure 5.
NNMT deficiency ameliorates renal inflammation in the UUO model. Renal NNMT mRNA expression (A), inflammation-related genes (B), renal NAD + metabolites (D), and mRNA expression of sirtuins (E) were measured in the kidneys of NNMT-KO mice and WT littermates two days after UUO induction. The data represent means ± SEM (n = 4–8 per group). (C) IHC staining and quantitative analysis for F4/80. The data represent means ± SEM (n = 3–8 per group). (F) The acetylation status of NF-κB in the kidney after UUO induction (n = 4 per group). Full-length blots/gels are presented in Supplementary Fig. 7. UUO, unilateral ureter obstruction; NNMT, nicotinamide N-methyltransferase; Il-1β, interleukin 1-beta; MCP-1, monocyte chemotactic protein-1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; NAM, nicotinamide; NMN, nicotinamide mononucleotide; NAD + , nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; MNA, 1-methylnicotinamide; N-Me-2PY, N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide; N-Me-4PY, N-methyl-4-pyridone-3-carboxamide; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus WT mice; †P < 0.05, ††P < 0.01 versus the same genotype control mice (sham-operated kidney).