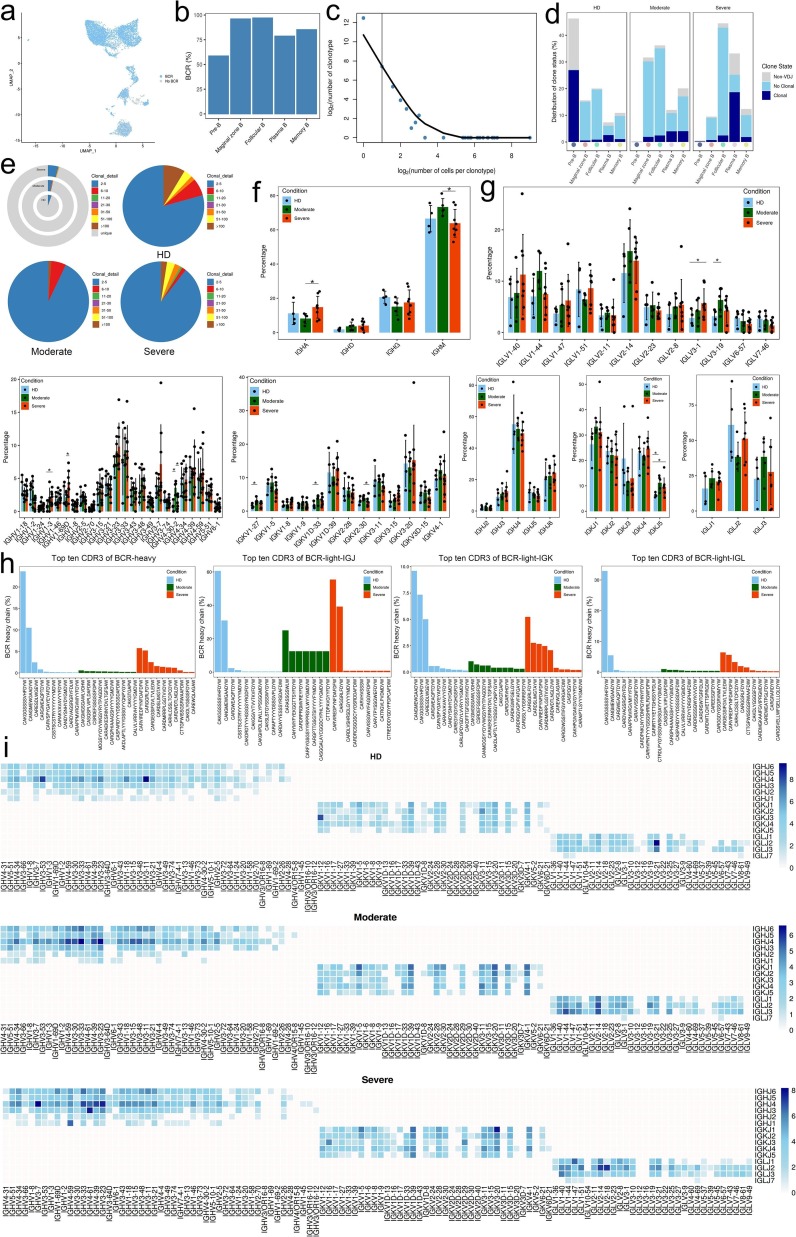
Fig. 8.
Expanded BCR clones and selective usage of V(D)J genes. a, The UMAP of B cells derived from PBMCs. The UMAP of B cells is colored based on BCR detection. B cells expressing BCR with blue dots indicate cells with BCR and gray dots indicate cells without BCR. b, Bar plot showing percentage of B cells expressing BCR detection in each B cell cluster. c, The association between the number of B cell clones and the number of cells per clonotype. The dashed line separates nonclonal and clonal cells. The x-axis is log2 (the number of cells per clonotype), and the y-axis is the number of cells clonotype. The dashed line at x = 1 represents the clonotype of BCR with nonclonal on the left and clonal cells on the right. The regression curve algorithm is LOESS fitting. d, Bar plot showing the distribution of the clone state of B cells in each cluster of HDs (n = 4), convalescent patients with moderate COVID-19 (n = 5), convalescent patients with severe COVID-19 (n = 8) groups. Clonotype copy number greater than 2 is clonal while clonotype copy number equal to 1 is nonclonal, and no clonotype represent non-BCR is marked as Non-VDJ. e, The clonal status percentage of B cells (top left) and percentage of different levels of clonal B cells (top right, bottom left and bottom right) across B cells derived from HDs (n = 4) and convalescent patients with moderate COVID-19 (n = 5), convalescent patients with severe COVID-19 (n = 8). f, Bar plot showing the percentages of IGHA, IGHD, IGHG and IGHM in each condition, with error bars representing ± s.e.m. for HDs (n = 4) and 13 patients, convalescent patients with moderate COVID-19 (n = 5) and convalescent patients with severe COVID-19 (n = 8). Higher column represents more gene appears in the group. All differences with P < 0.05 are indicated and were analyzed using unpaired two-sided t-test. g, Usage of some IGHV (top left), IGHJ (top right), IGKV (middle left), IGKJ (middle right), IGLV (bottom left) and IGLJ (bottom right) genes across conditions of HDs (n = 4) and convalescent patients with moderate COVID-19 (n = 5), convalescent patients with severe COVID-19 (n = 8). The average percentages of the genes in each condition are showed with the height of the column. Conditions are shown in different colors. Error bars represent ± s.e.m. for 4 HDs and 13 patients. Higher column represents more gene appears in the group. All differences with P < 0.05 are indicated and were analyzed using unpaired two-sided t-test. Error bars represent ± s.e.m. for 4 HDs and 13 convalescent patients. h, The top ten CDR3 usages of protein sequences of heavy chain and light chain are shown across groups of HDs (n = 4), convalescent patients with moderate COVID-19 (n = 5), convalescent patients with severe COVID-19 (n = 8). Each bar is colored by condition identity. Shared CDR3 sequences are in a red front. i, Heat maps showing IGH/K/L rearrangement differences across conditions of HDs (n = 4) and convalescent patients with moderate COVID-19 (n = 5), convalescent patients with severe COVID-19 (n = 8). Colors indicate the log2((usage count) + 1) of specific V-J gene pairs. Darker color represents more gene combination appear.