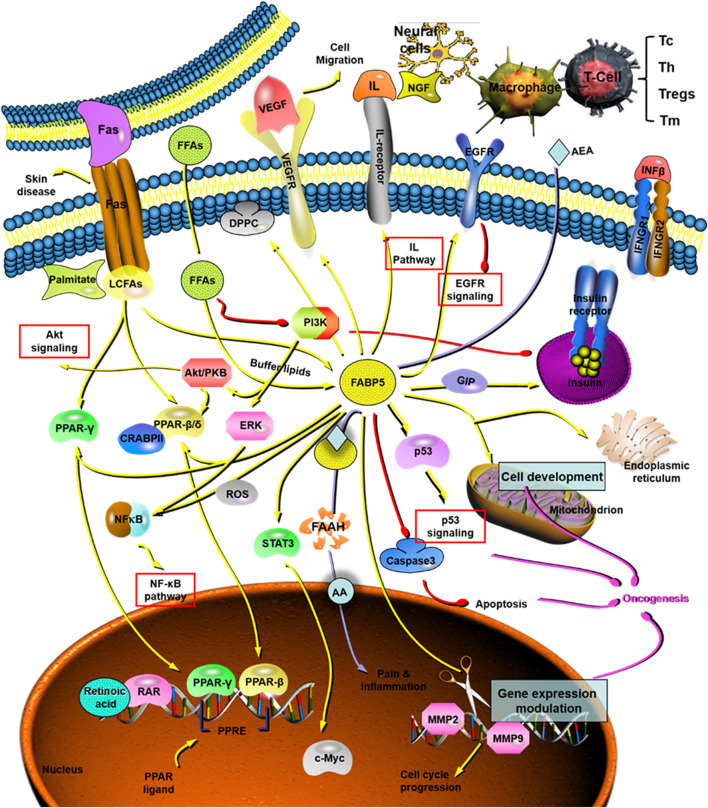
FIGURE 7.
The role and mechanism of FABP5 in tumorigenesis and cancer development. FABP5 plays critical roles in cancer initiation and progression through the AKT pathway, NF-κB pathway, IL pathway, EGFR pathway, p53 pathway, and so on. AA: arachidonic acid; AEA: endocannabinoid anandamide; CRABP: cytosolic retinoic acid-binding protein; DPPC: dipalmitoyl phosphatidyl choline; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptors; ERK: extracellular regulated protein kinases. FAAH: fatty acid amide hydrolase; FAS: fatty acids; FFA: free fatty acids; FABP5: fatty acid binding protein 5; GIP: glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide; IFN: interferon; IL: interleukin; LCFAS: long-chain fatty acids; MMP: matrix metalloproteinase; NF-κB: nuclear factor-kappa B; NGF: nerve growth factor; PI3K: phophatidylinositol-3-kinase; PPAR: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; PPRE: proliferator-activated response element; RAR: retinoic acid receptor; ROS: reactive oxygen species; STAT: signal transducer and activator of transcription; Tc: cytotoxic T cell, CD8+ T cell; Th: helper T cell, CD4+ T cell; Treg: regulatory T cell; Tm: memory T cell.