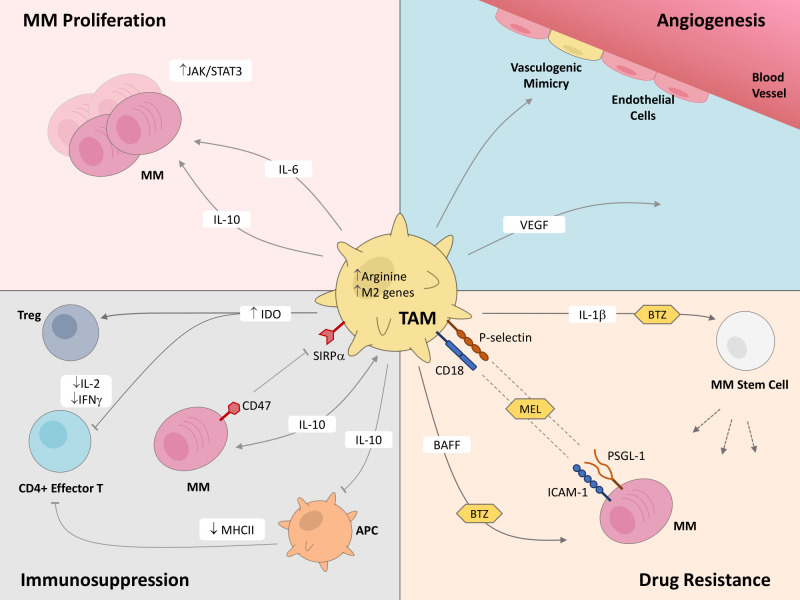
Figure 1.
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) play critical roles in multiple myeloma (MM) disease progression. This figure highlights the known effects that TAMs exert on MM cells and cells within the MM tumor microenvironment, through both secretion of molecules and contact-based surface interactions, which support proliferation and survival, angiogenesis, immunosuppression, and drug resistance in MM. APC, antigen presenting cell; BAFF, B-cell activating factor; BTZ, bortezomib; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; IL, interleukin; JAK/STAT3, Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription proteins; MEL, melphalan; MHCII, major histocompatibility complex class II; PSGL-1, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1; SIRPα, signal-regulatory protein α; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.