Figure 5: TLR7 is required for IFN signaling-dependent expansion of B cells producing EPCR–LBPA-reactive aPLs.
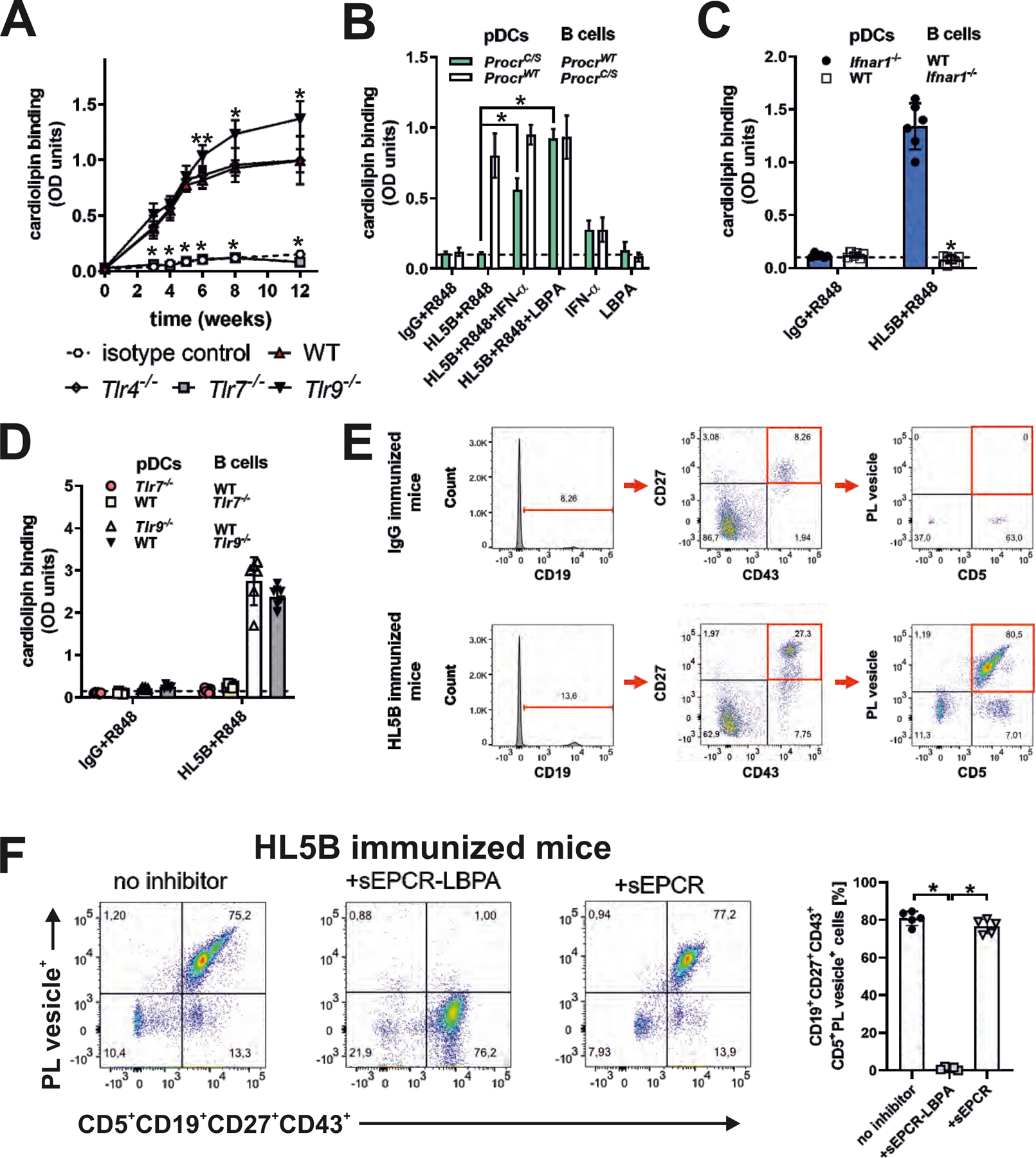
(A) Mice of the indicated genotypes were immunized with aPL HL5B or isotype-matched control IgG and serum anti-cardiolipin titers were determined at the indicated times; n=10, *P<0.005 for Tlr7−/− or Tlr9−/− versus WT; one-way ANOVA. (B to D) Isolated spleen pDCs and B cells from the indicated mouse strains were co-cultured in the presence of TLR7 agonist R848, aPL HL5B, IFN-α, and LBPA as indicated for 8 days, followed by determination of anti-cardiolipin titers; n=6, *P<0.0001; one-way ANOVA. (E) Gating for CD5+CD19+CD27+CD43+ memory type B1a cells and demonstration of their reactivity with negatively charged fluorescent phospholipid vesicles specifically in mice immunized with aPL HL5B, but not isotype-matched IgG. (F) Competition of sEPCR–LBPA, but not sEPCR with phospholipid vesicle binding to B1a cells; n=5, *P<0.0001; one-way ANOVA.
