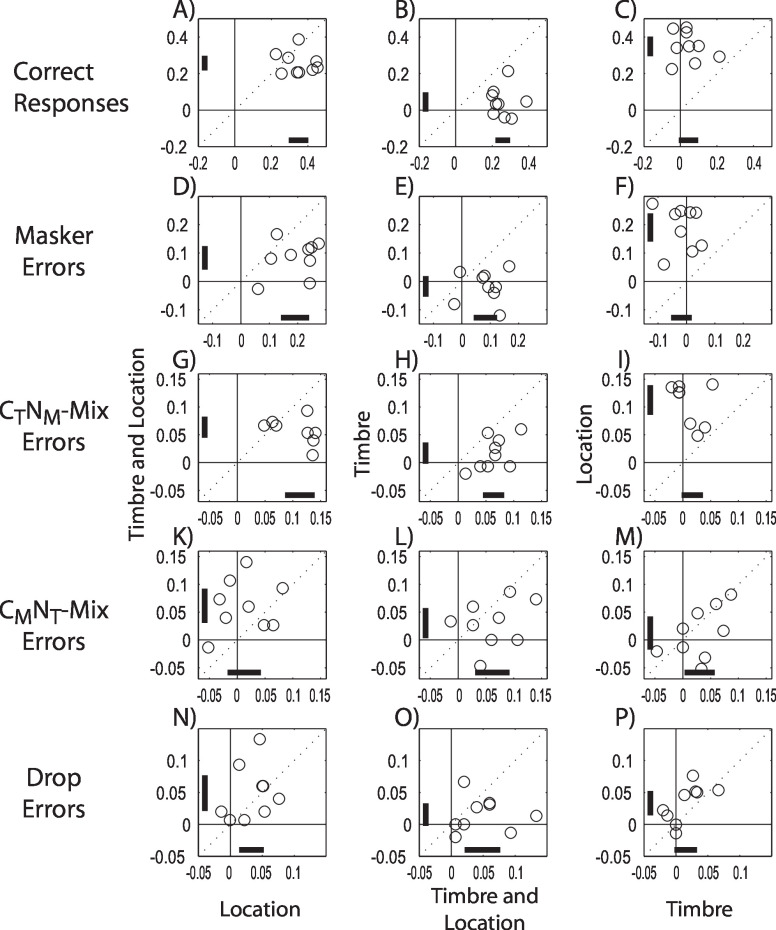
FIG. 4.
Individual subject spatial gains (see text for definition) in correct performance, and masker, mix, mix, and drop errors contrasted across task conditions. Individual subjects all show large improvements in overall performance with spatial separation of the target and masker when they know the target location but not when they are attending to the target timbre. Overall, spatial separation of target and masker reduces response errors of all kinds (produces positive spatial gains); however, when listeners attend to the timbre, there is no significant reduction in masker errors. Each row compares the reduction in errors with spatial separation for one type of response error (correct performance, masker, mix, mix, and drop errors in top, second, third, fourth, and bottom rows, respectively). Within each panel, each point compares results for one of the nine individual subjects across two different task conditions. The horizontal and vertical bars within each panel show the 95% confidence intervals for the group mean of the spatial gain in the corresponding dimension. Left column: timbre-and-location vs location. Center column: timbre vs timbre-and-location. Right column: location vs timbre.