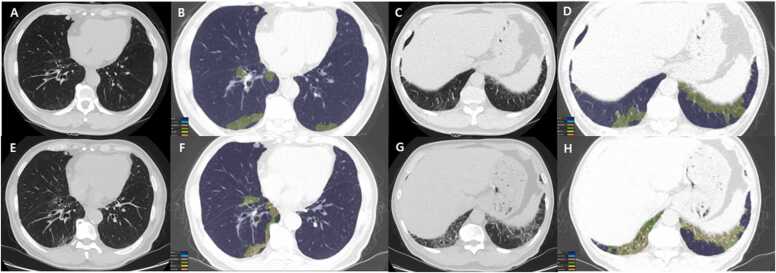
Fig. 1.
Serial chest CT scans from a 68-year man with CTD (rheumatoid arthritis)-interstitial lung abnormality. (a-d) Baseline chest CT (top row) images obtained from lower lung zone show lung lesions composed of mild ground-glass opacity in subpleural region. The color-coded overlay (b & d) on CT images, by enabling automatic volume segmentation of lung parenchymal abnormalities, allows quantification of ground-glass opacity (3.14% involvement of total lung volume) and reticular (0.29% involvement of total lung volume) lesions.(e-f) Five-year follow-up CT (bottom row) images demonstrate changing pattern and distribution of lung abnormalities; decrease in ground-glass opacity (from 3.14% to 2.84%, green areas) and increase in reticulation (from 0.29% to 2.33%, yellow areas), when comparing (b & f) and (d & h) from each other.