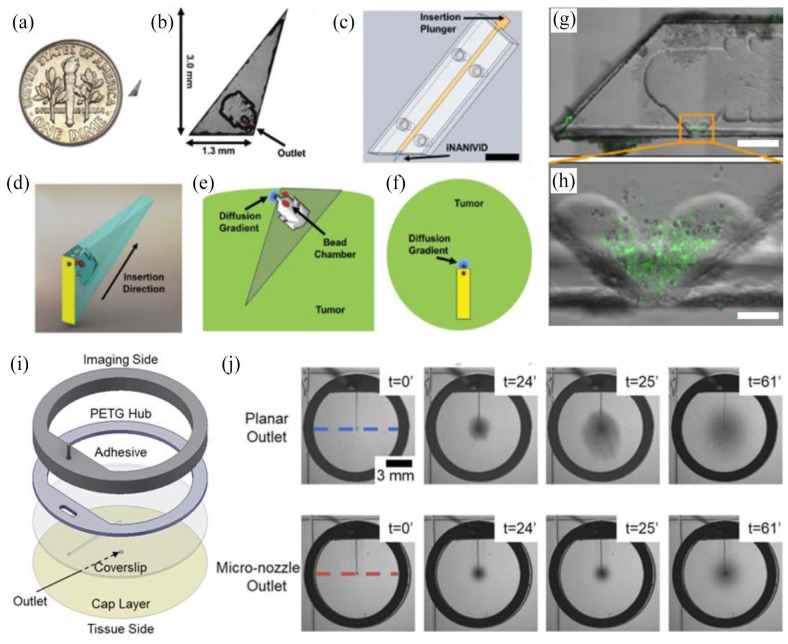
Figure 3.
Implantable devices for simultaneous imaging and drug delivery in vivo: (a) the induction nano-intravital device (NANIVID) next to a US dime, (b) the NANIVID is designed to penetrate solid tumor tissue for passive delivery, (c) insertion is facilitated by an applicator which aligns the device with the tumor surface, (d) a 3D render demonstrates the device orientation during insertion, (e) a cross-sectional view of an implanted NANIVID depicts the location of the outlet and generated diffusion gradient, (f) top–down view of the insertion site for imaging, (g) alternative NANIVID design for cell collection, scale bar = 500 μm, (h) magnified view of the device outlet where green fluorescing cells were collected, scale bar = 100 μm, (i) exploded view of the microfluidic imaging window for active reagent delivery, (j) demonstration of improved dye localization in hydrogel tissue mimics with a micro-nozzle outlet. (A color version of this figure is available in the online journal.)
Source: Adapted from Williams et al.166,174 and Head et al. 177