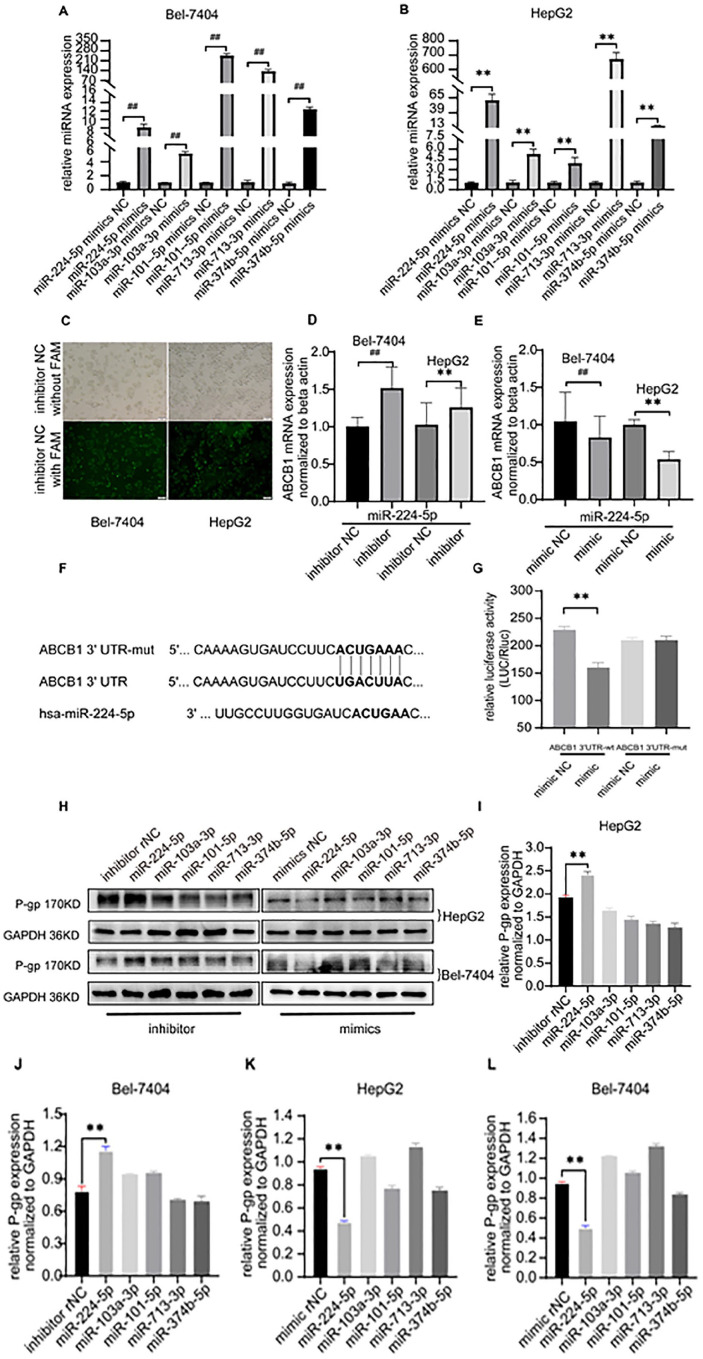
Figure 4.
(A–L) MiR-224-5p directly regulated the ABCB1 mRNA and further downregulated P-gp expression in human HepG2 and Bel-7404 cells. (A and B) Relative expression of 5 miRNAs in cells transfected with mimics or mimics NC. (C) Fluorescent images of human HepG2 and Bel-7404 cells transfected with FAM-labeled inhibitors or inhibitors NC. (D) Real time qPCR showed that relative ABCB1 mRNA levels in human HepG2 and Bel-7404 cells with miR-224-5p inhibitor was slightly up-regulated relative to cells with miR-224-5p inhibitor NC. (E) Relative low level of ABCB1 mRNA was observed in human HepG2 and Bel-7404 cells with miR-224-5p mimic compared with cells with miR-224-5p mimic NC. (F) The sequence of miR-224-5p and its potential binding site of ABCB1 3′UTR. (G) Dual luciferase reporter assay showed that miR-224-5p can directly target ABCB1 3′UTR. Renilla luciferase was used as internal reference. (H) Western blot analysis indicated that P-gp expression was overexpressed in human HepG2 and Bel-7404 cells only transfected with miR-224-5p inhibitor and was inhibited in cells only transfected with miR-224-5p mimic. GAPDH was used for internal control. (I–L) Relative P-gp expression of 5 miRNAs in HepG2 and Bel-7404 cells transfected with mimics or inhibitors. Data were showed as Mean ± SD. Each experiment was repeated 3 times. ##P < .05, **P < .01.