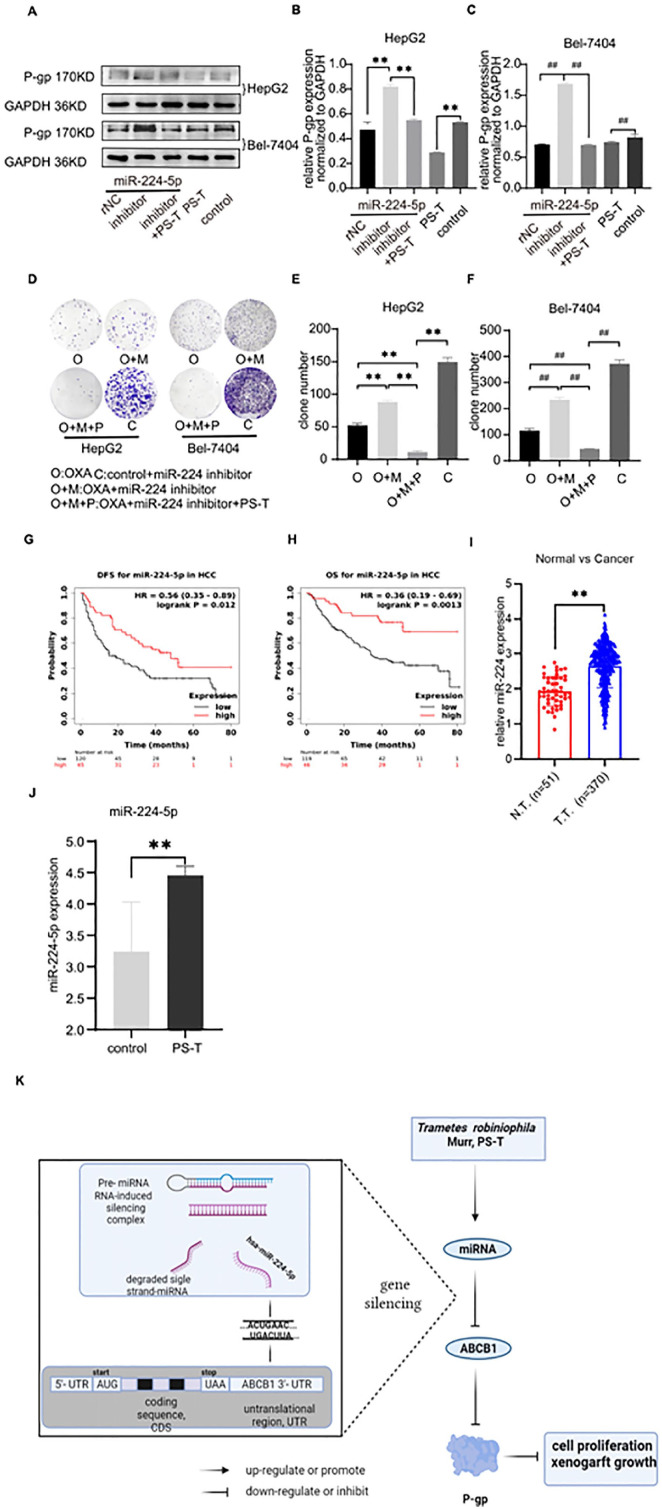
Figure 5.
(A–K) PS-T increased the sensitivity of human hepatoma cells to OXA by regulating miR-224-5p/ABCB1/P-gp axis. (A) Western blot analysis showed that PS-T could down-regulate P-gp expression in human HepG2 or Bel-7404 cells with miR-224-5p inhibitor, respectively. GAPDH was considered as internal control. (B and C) Relative P-gp expression in human HepG2 and Bel-7404 cells with miR-224-5p inhibitor or inhibitor NC. (D) The photographs of clones of human HepG2 and Bel-7404 cells transfected with miR-224-5p inhibitor. The results showed the ability of inhibiting cell proliferation of OXA was recovered after the treatment of PS-T. (E and F) Clone numbers of human Bel-7404 and HepG2 cells were counting by Image J software. (G and H) Survival analysis showed that HCC patients with high expression of miR-224-5p had a better overall survival (HR = 0.36 [0.19-0.69], logrank P = .0013) and disease-free survival (HR = 0.56 [0.35-0.89], logrank P = .012). (I) MiR-224-5p was highly expressed in tumor tissue compared with normal tissue in patients with HCC in TCGA database (N.T. means normal tissues; T.T. means tumor tissues). (J) Real time qPCR indicated that PS-T can upregulate miR-224-5p expression compared with control group. Beta-actin was regarded as negative control. (K) The overview diagram of mechanism: PS-T strengthens the sensitivity of human hepatoma cells to OXA via the miR-224-5p/ABCB1/P-gp axis. The picture was made by BioRender (https://biorender.com/). ##P < .05, **P < .05.