Figure 1.
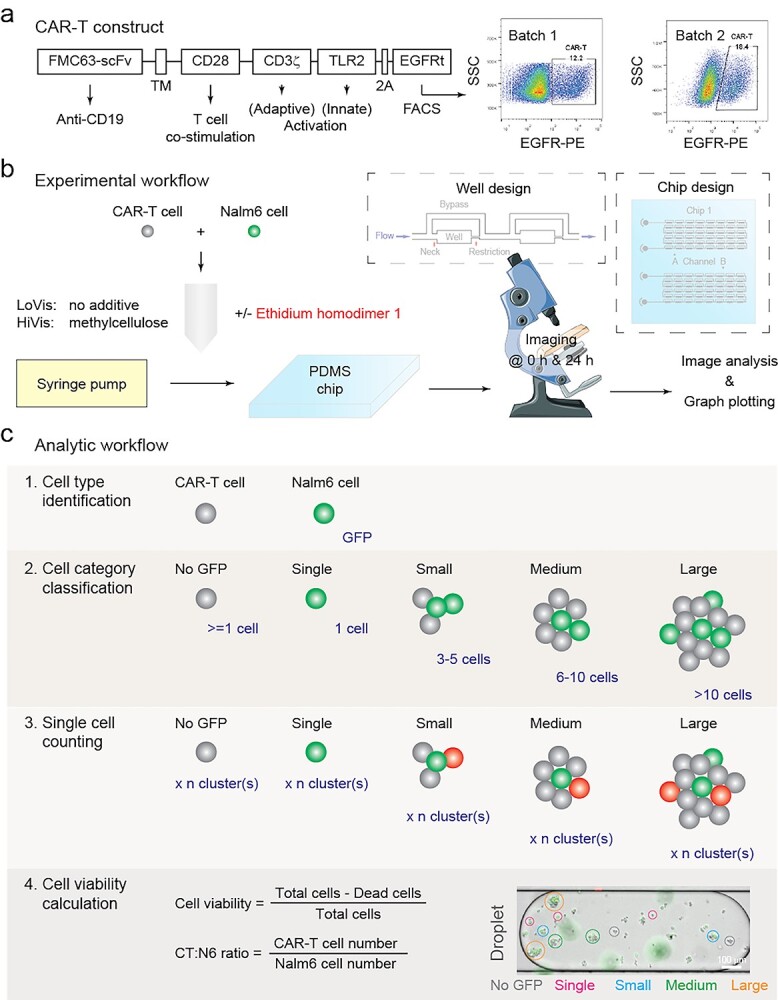
Paradigm of this study. (a) CAR-T construct design and FACS characterization. CAR was constructed with the CD19-targeting FMC63-scFv domain (FMC63-sFv), the CD28 transmembrane domain (TM), the CD28 endodomain (CD28), CD3ζ signaling domain (CD3ζ), the Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), the 2A self-cleaving peptide (2A) and the extracellular and transmembrane domains of truncated human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFRt). CAR-T cells were purified 12 h post-transduction using anti-human EGFR antibody and side scattering (SSC); the percentage of CAR-T cells in the population of all transduced T cells was indicated. (b) Experimental workflow of this study. CAR-T and Nalm6 cancer cells were mixed and loaded on chip, followed by 24 h incubation and imaging. The design of the chip and its wells was shown in the insets. (c) Analytic workflow of this study. Nalm6 cells were initially identified by GFP fluorescence, followed by cell category classification, cell counting and viability calculation. Cell category classification was arbitrary as shown in the inset. Dead cells were indicated by the red fluorescent dye ethidium homodimer 1 (EH1); for EH1-free assays, cell viability was calculated by the difference of the number of Nalm6 cells before and after treatment.
