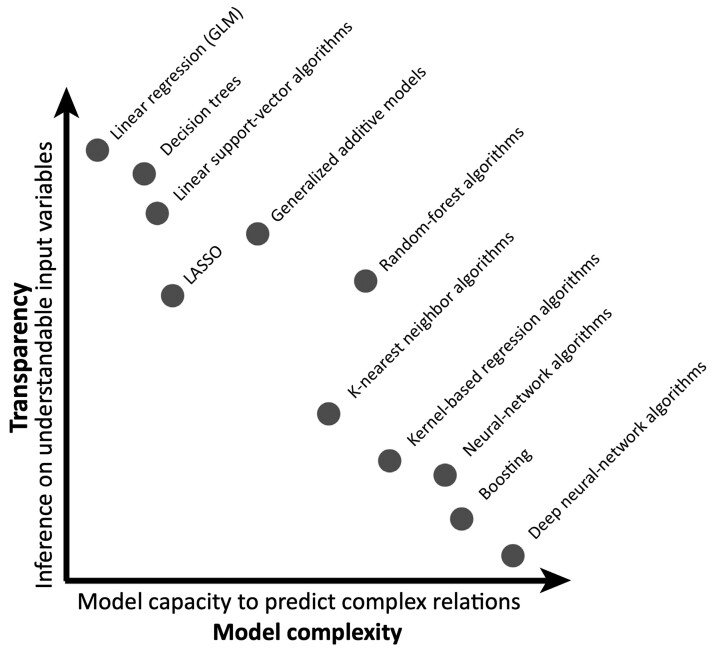
Figure 6.
Comparison of various learning algorithms with respect to their model transparency and complexity. Model transparency here refers to the interpretability of input variables and thus the potential scientific insight and mechanistic understanding that can be gained. More complex models, in return, maximize the predictive power. Altogether, increased transparency may come at the cost of decreased model complexity and associated decreased predictive power and vice versa. Figure adapted from Bzdok and Ioannidis,212 with permission.