FIGURE 1.
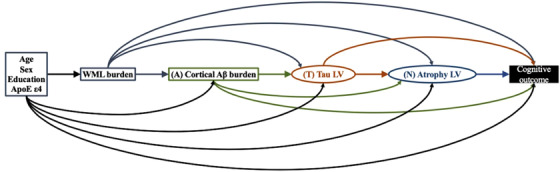
A priori hypothesized biomarker pathways by which amyloid beta (Aβ)–tau–atrophy biomarkers might mediate the association of Alzheimer's disease (AD) risk factors and cognition. Rectangles represent manifest variables and ellipses represent latent variables. Each single‐headed arrow denotes a hypothesized unidirectional effect of one variable on another. For graphical simplicity, age, sex, education, and apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 is grouped although each AD risk factor is separately hypothesized to have unidirectional effect on white matter lesion (WML), cortical Aβ burden, tau latent variable (LV), atrophy LV, and cognitive outcome. Our analysis is premised on a conceptual Aβ–tau–atrophy pathologic pathway thought to mediate the association of AD risk factors and cognition. A priori, age, sex, years of education, and presence of APOE ε4 allele were specified to have direct effects on global Aβ, regional tau, regional atrophy, and WML, in addition to their direct effects on cognition. WML was hypothesized to have a direct effect on global Aβ, regional tau, and regional atrophy, in addition to its direct effect on cognition. Global Aβ was hypothesized to have a direct effect on regional tau and regional atrophy, in addition to its direct effect on cognition. In turn, the regional tau was hypothesized to have direct effect on regional atrophy, together with the direct effects of regional tau and regional atrophy on cognition. We note that the regional specificity of Aβ pathology was examined by including regional Aβ burden from all 31 ROIs instead of limiting the Aβ construct to the global cortical Aβ burden in the partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS‐SEM). The estimated latent construct for the regional Aβ burden in the final PLS‐SEM involved all but bilateral entorhinal, amygdala, and hippocampus regions, suggesting the effect of Aβ being distributed across the cortex rather than localized in specific cortical regions in this cohort of all Aβ‐positive individuals. Therefore, Aβ construct of all PLS‐SEMs in this study was limited to global cortical Aβ burden.
