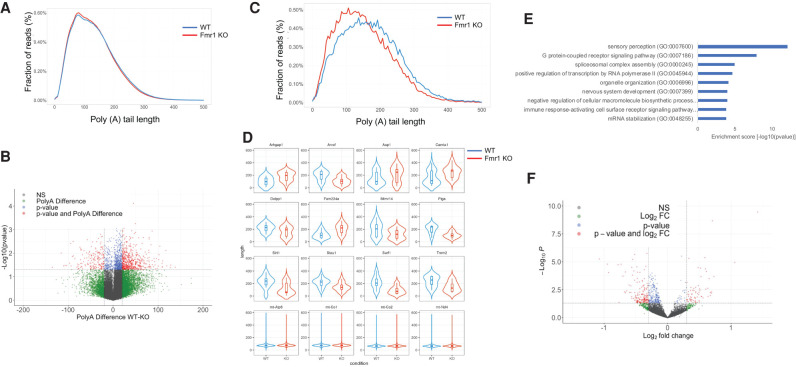
FIGURE 3.
Determination of poly(A) tail length in Fmr1 KO cortex by direct RNA sequencing using a nanopore platform. (A) Distribution of poly(A) tail lengths of RNAs in WT and Fmr1 KO brain cortex as a fraction of total reads excluding mitochondrial RNAs. (B) Volcano plot showing RNAs that undergo poly(A) tail size changes in WT compared to Fmr1 KO brain cortex. In red, transcripts that show differential poly(A) tail lengths of at least 20 residues (P < 0.05; two tailed t-test). (C) Distribution of poly(A) tail lengths of differentially polyadenylated transcripts (n = 736) versus fraction of total reads in WT and Fmr1 KO cortex. (D) Violin plots with box plot for top differential poly(A) transcripts with P < 0.05 (two tailed t-test) as in B; reads for each transcript were pooled for the two genotypes. (E) Gene Ontology (GO) term analysis of RNAs that undergo poly(A) tail size changes in Fmr1 KO cortext compared to WT. (F) Volcano plot of RNAs that have altered expression levels in Fmr1 KO cortext compared to WT. For all comparisons, 2 WT and 3 Fmr1 KO cortexes were analyzed.