Figure 4: α-Synuclein (α-syn)-tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) colocalization indices in affected or unaffected carriers of SNCA or GBA mutations.
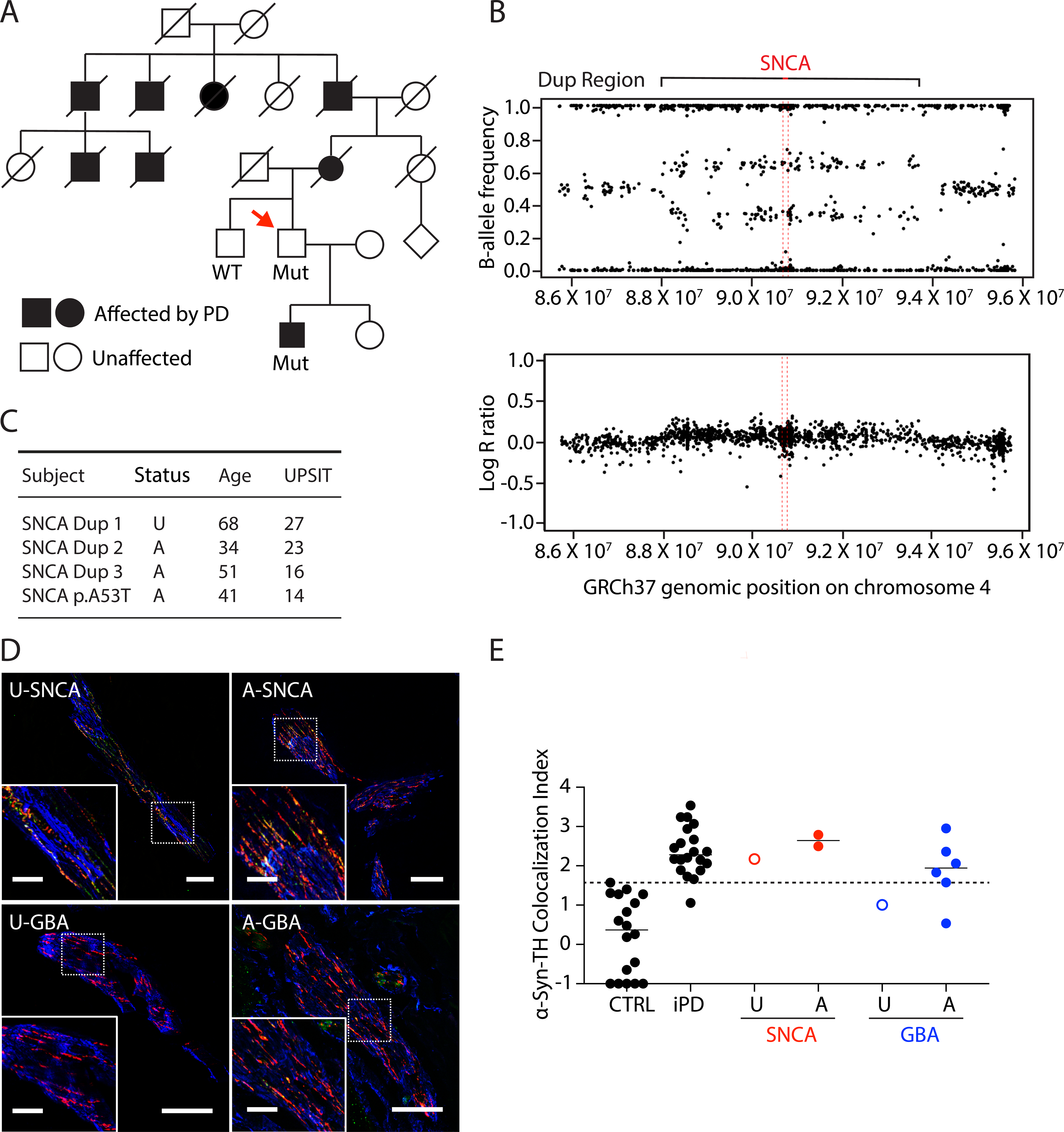
(A) Pedigree of an unaffected SNCA duplication carrier. Red arrow shows the patient. Filled in symbol indicates affected individual. (B) Genome sequencing results of the unaffected SNCA duplication carrier. (C) Clinical characteristics of the unaffected SNCA duplication carrier and 3 affected SNCA duplication carrier. SNCA Dup 2 is the first-degree relative of the unaffected SNCA duplcation carrier, in the filled square in (A). These patients had available University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test (UPSIT) data. (D) Confocal microscopic images of immunoreactive α-syn (green), tyrosine hydroxylase (TH, red), smooth muscle actin (blue), and α-syn colocalized with TH (yellow) in arrector pili muscles from skin biopsies. The images are from the patients who are unaffected (U) or affected (A) carriers of SNCA or GBA mutations. Scale bars = 50 μm for main image, 20 μm inserts. (E) Individual data for control subjects (CTRL), patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease (iPD), and unaffected (U) or affected (A) with SNCA or GBA genotypic abnormalities. Dashed line shows the upper limit of the CTRL. Horizontal lines indicate median values in each group. Note that SNCA abnormalities are associated with increased α-syn-TH colocalization indices even if the individual is unaffected.
