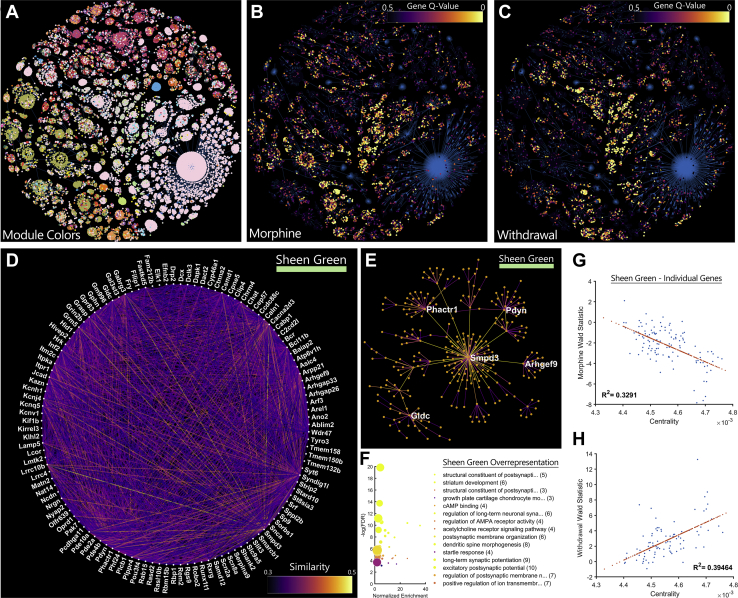
Figure 4.
A cAMP-regulated gene network is inhibited by morphine tolerance and induced by withdrawal. (A) Genes are coded by module color and projected into a two-dimensional minimum spanning tree. The same genes are coded by differential expression (q value) data during (B) morphine tolerance and (C) withdrawal. Functionally related genes tend to cluster in modules. (D) The Sheen Green gene module is displayed using a circle layout. Line brightness represents gene similarity as calculated by weighted gene coexpression network analysis. (E) The top 5 most central genes in each network are highlighted in a hub-and-spoke representation of the network. (F) Overrepresentation analysis of genes in this network provides clues to their functional relevance. Many genes are downstream targets of cAMP signaling or promote reorganization of synapses and the actin cytoskeleton. Gene sets are sorted by normalized enrichment, while color represents −log(FDR). Centrality in the Sheen Green network is highly correlated to differential expression for both (G) morphine tolerance and (H) withdrawal. cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; FDR, false discovery rate.