Extended Data Fig. 4. TRPM2 is required for CD36 activation in macrophages induced by oxLDL.
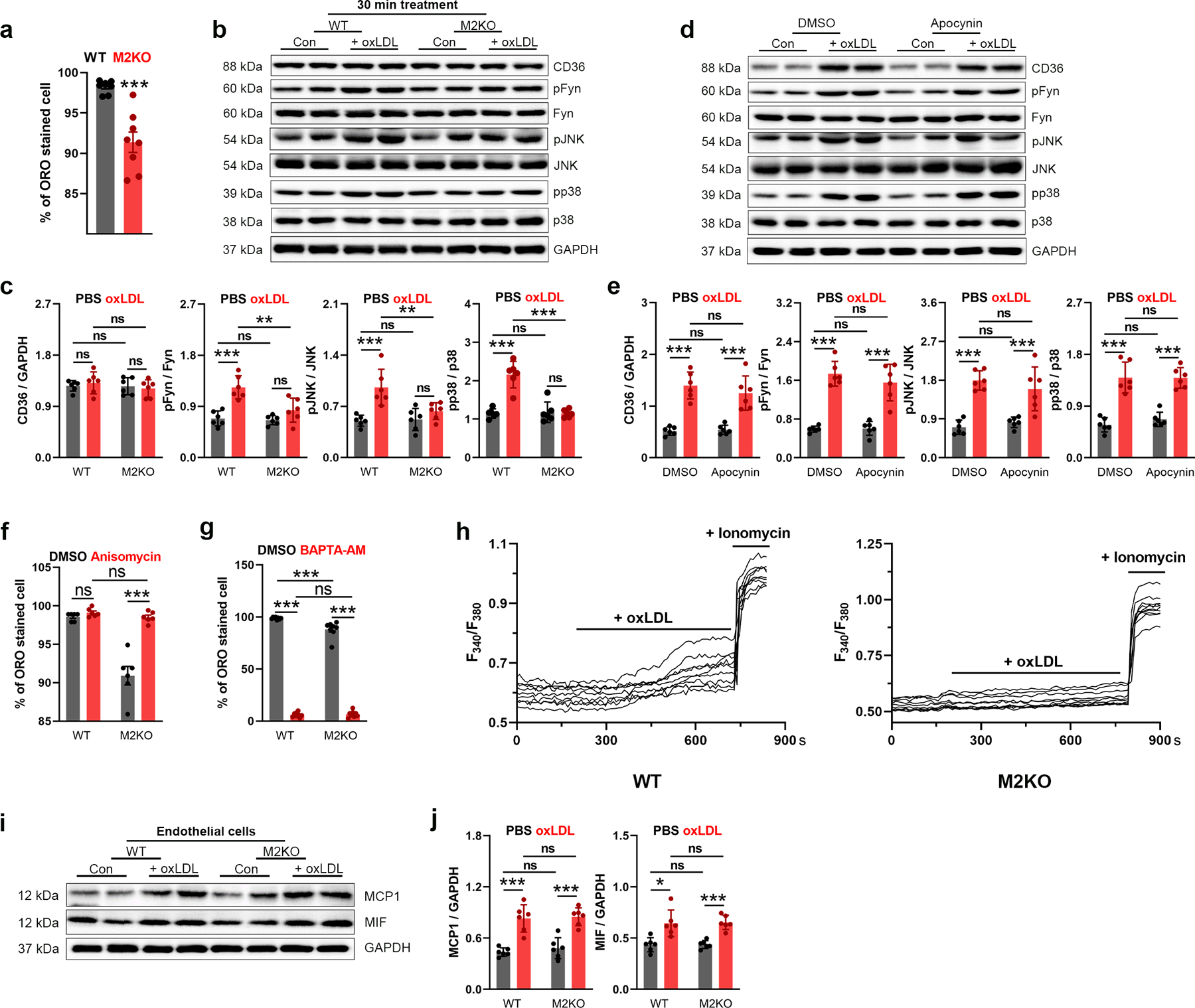
(a) Quantification of Fig 4a by counting percentage of Oil red O staining macrophages (n=8/group). (b, c) 30-min oxLDL treatment (50 μg/ml) induce the activation of CD36 signaling without upregulating CD36 expression. Representative WB analysis of CD36, pFyn, pJNK and pp38 expression in macrophages after oxLDL treatment for 30 min (n=6/group). (d, e) NADPH oxidase inhibitor apocynin does not inhibit CD36 activation induced by 24-h oxLDL treatment (50 μg/ml) in macrophages isolated from wild-type (WT) mice. Representative WB analysis of CD36, pFyn, pJNK and pp38 expression in macrophages after oxLDL treatment for 24 h (n=6/group). (f) Quantification of Fig 4k by counting percentage of Oil red O staining macrophages (n=6/group). (g) Quantification of Fig 4o by counting percentage of Oil red O staining macrophages (n=8/group). (h) A set of original Fura-2 real time recording traces without normalization during oxLDL treatment as in Fig 4o. (i, j) Trpm2 deletion does not influence the production of MCP1/MIF in endothelial cells isolated from aorta in response to 24-h oxLDL treatment (50 μg/ml). Representative WB analysis of MCP1 and MIF expression in endothelial cells after oxLDL treatment for 24 h (n=6/group). (ns: no statistical significance; *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001; ANOVA, two-tailed, Bonferroni’s test; mean ± SEM).
