Extended Data Fig. 5. TRPM2 is required for CD36 activation in macrophages induced by TSP1.
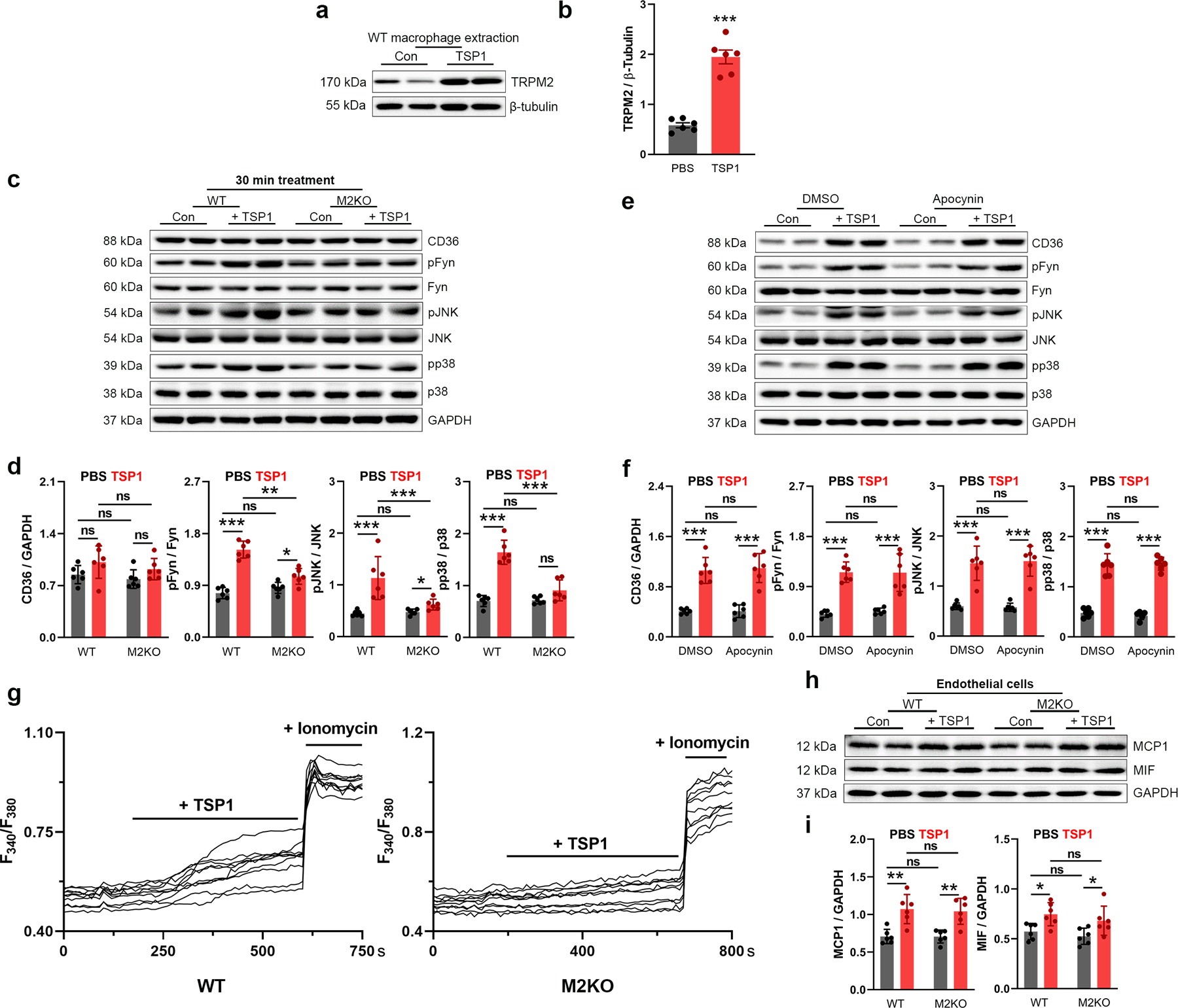
(a, b) Representative WB analysis of TRPM2 expression in macrophages isolated from WT mice with or without the treatment of TSP1 (10 μg/ml) for 24 h (n=6/group). (c, d) 30-min TSP1 (10 μg/ml) treatment induce the activation of CD36 signaling without upregulating CD36 expression. Representative WB analysis of CD36, pFyn, pJNK and pp38 expression in macrophages after TSP1 treatment for 30 min (n=6/group). (e, f) NADPH oxidase inhibitor apocynin does not inhibit CD36 activation induced by 24-h TSP1 (10 μg/ml) treatment in macrophages isolated from wild-type (WT) mice. Representative WB analysis of CD36, pFyn, pJNK and pp38 expression in macrophages after TSP1 treatment for 24 h. (g) A set of original Fura-2 real time recording traces without normalization during TSP1 treatment as in Fig 5g. (h, i) Trpm2 deletion does not influence the production of MCP1/MIF in endothelial cells isolated from aorta in response to 24-h TSP1 (10 μg/ml) treatment. Representative WB analysis of MCP1 and MIF expression in endothelial cells after TSP1 treatment for 24 h (n=6/group). (ns: no statistical significance; *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001; ANOVA, two-tailed, Bonferroni’s test; mean ± SEM).
