Extended Data Fig. 8. Graphic illustration, the activation of CD36 and TRPM2 form a positive feedback loop in atherogenesis.
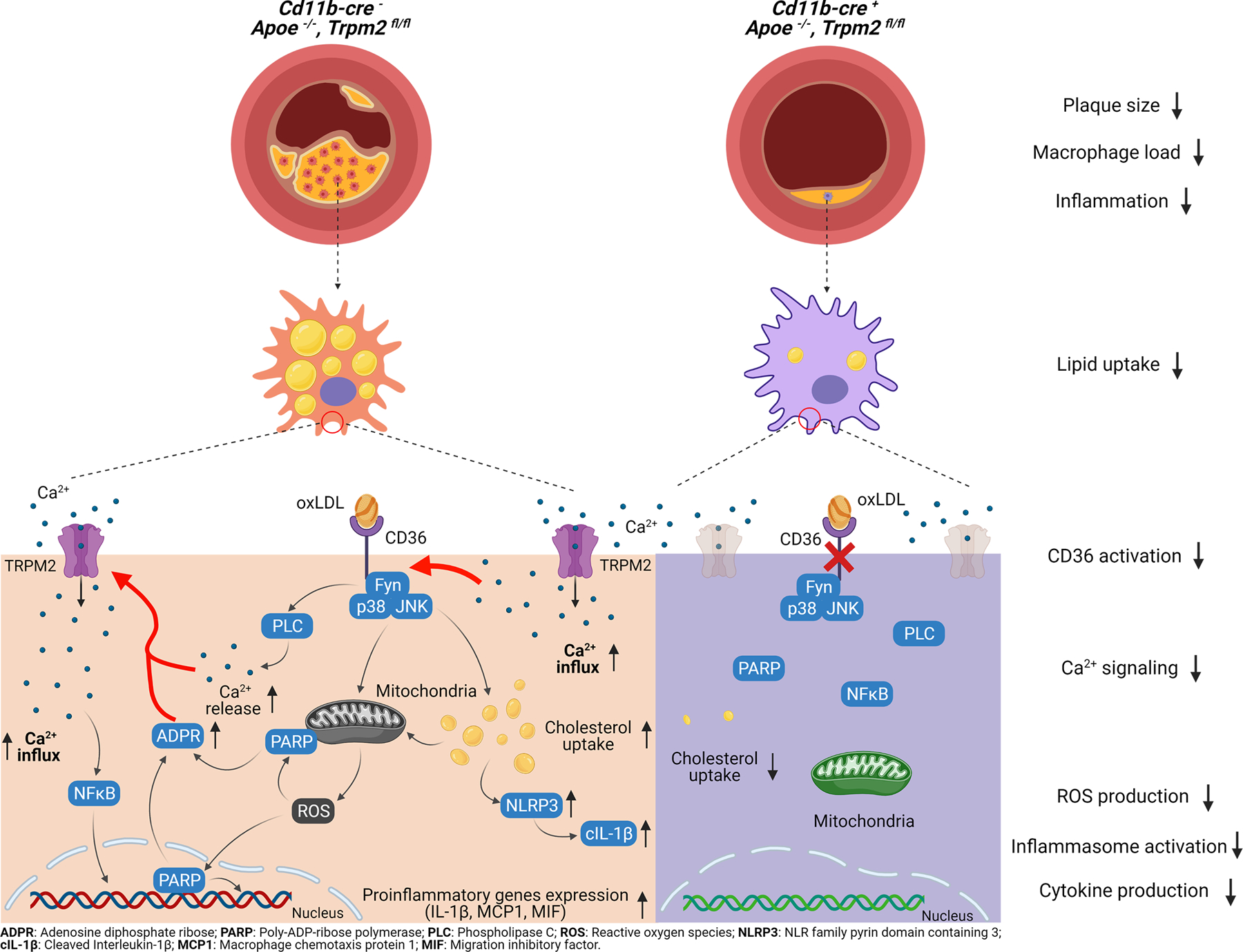
In summary, we found that: (1) Global Trpm2 deletion and macrophage-specific Trpm2 deletion protect against atherosclerosis in Apoe−/− mice fed with a high-fat diet (HFD). (2) Trpm2 deficiency in macrophages inhibits atherogenesis by inhibiting macrophage infiltration and minimizing foam cell formation. (3) TRPM2 activation is required for CD36-induced oxLDL uptake and subsequent inflammatory responses in macrophages. (4) The ligands of CD36, oxLDL and TSP1, activate TRPM2, thereby perpetuating TRPM2-CD36 inflammatory cycle in atherogenesis cascade. (5) Our data establish TRPM2-CD36 axis in macrophages as an important atherogenesis mechanism and TRPM2 as a promising therapeutic target for atherosclerosis
