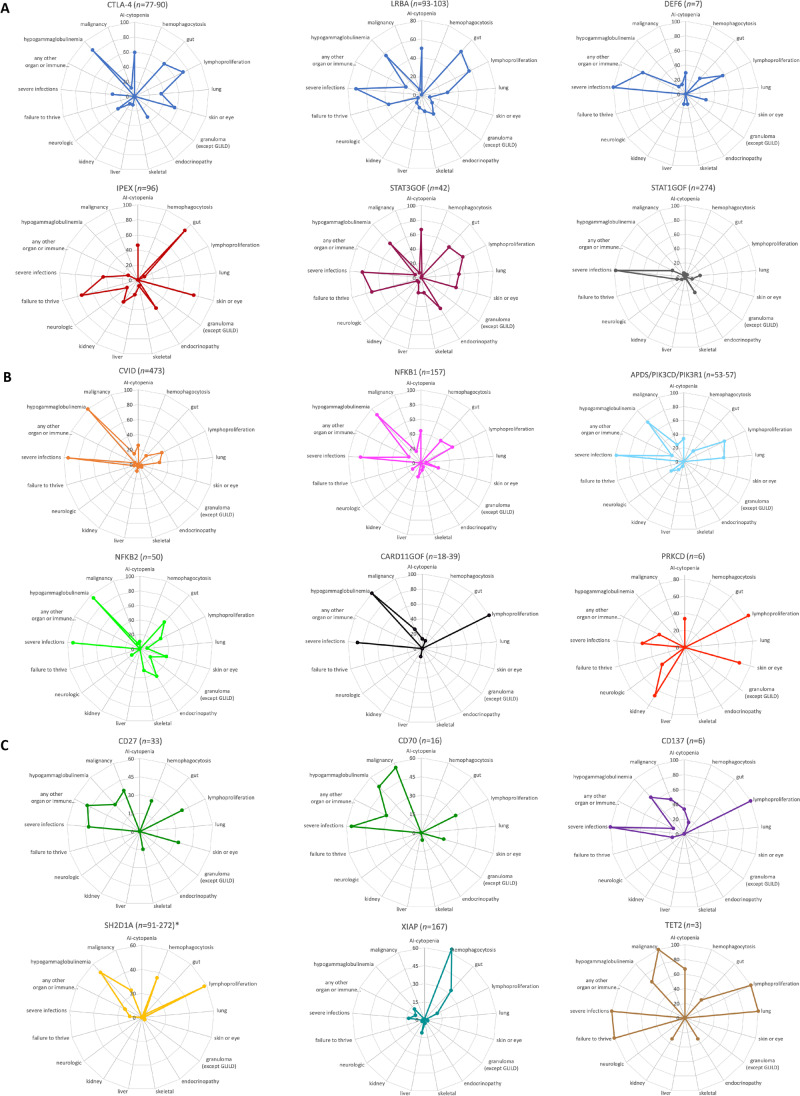
Fig. 2.
Immune deficiency and dysregulation phenotype patterns visualized by the IDDA2.1 kaleidoscope score for 18 exemplary IEI. The kaleidoscope function makes use of 17 out of 22 parameters documented in the IDDA score (terms #1–14; #20; #18; and #22, see Table 2), reduced to qualitative information about organ involvement and other features in a patient or a patient cohort, plotted according to the fixed order of parameters in a radar (spider) chart on 17 y-axes arranged in a circle. A Primary immune regulatory disorders, modified from [30] and supplemented with additional IEI, with data derived from reviews, case series, or large cohorts [1, 20, 31–36]; B Predominantly antibody deficiencies and combined immunodeficiencies [37–43]; C Diseases of immune regulation with EBV-susceptibility [44–50]. Data for part of the CARD11GOF and all of the XIAP plots were derived from unpublished data to appear in Hauck et al., 2021, and a manuscript in preparation by Yang and Burns et al., 2021, respectively. The patient numbers presented in the title of each plot may vary slightly regarding some features that were not available from all patients, but are always presented as a percentage on 17 y-axes. In the regular (22-parametric) IDDA score originally developed for LRBA deficiency [1], each criterion is semi-quantified per patient from 0 to 4◦, please refer to Table 2 for details. The full-length y-axis titles are autoimmune (AI)-cytopenia; hemophagocytosis | HLH (according to clinical AND lab criteria of the Histiocyte Society); gut, enteropathy | IBD (inflammatory bowel disease); lymphoproliferation | splenomegaly | hepatomegaly; lung, parenchymal lung disease | LIP (lymphocytic interstitial pneumonitis)| GLILD (granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease); skin or eye manifestations | eczema, uveitis, alopecia, vitiligo, other; granulomatous disease in any organ (other than GLILD); endocrinopathy | IDDM (insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus), thyroiditis, other; skeletal, arthritis | other musculoskeletal manifestations; liver, AI-hepatitis | cholangitis | pancreatitis; kidney, glomerulonephritis | nephropathy, tubulopathy; neurologic manifestations; failure to thrive | malresorption, wasting; severe infections | severe or opportunistic infections (excl. asymptomatic chronic infestation; excluding “EBV-susceptibility”); any other organ or immune dysfunction/malady (e.g., cardiomyopathy, kidney failure, autoinflammation, allergy); hypogammaglobulinemia and/or immunoglobulin substitution therapy; malignancy, lymphoma (separately added to IDDA score, not included in the score calculation); *, the footnote (asterisk) in SH2DA1 deficiency (XLP1) should indicate that, although this topic is debatable, the liver and kidney involvement in fulminant infectious mononucleosis was not counted under immune dysregulation (#10–11), likewise the CNS involvement in patients with HLH and XLP1 was not counted as organ-specific immune dysregulation (#12), and aplastic anemia observed in patients with XLP1 was not counted as autoimmune cytopenia (#1) to distinguish their pathogenesis from “primarily” immune-mediated organ manifestations in PIRDs