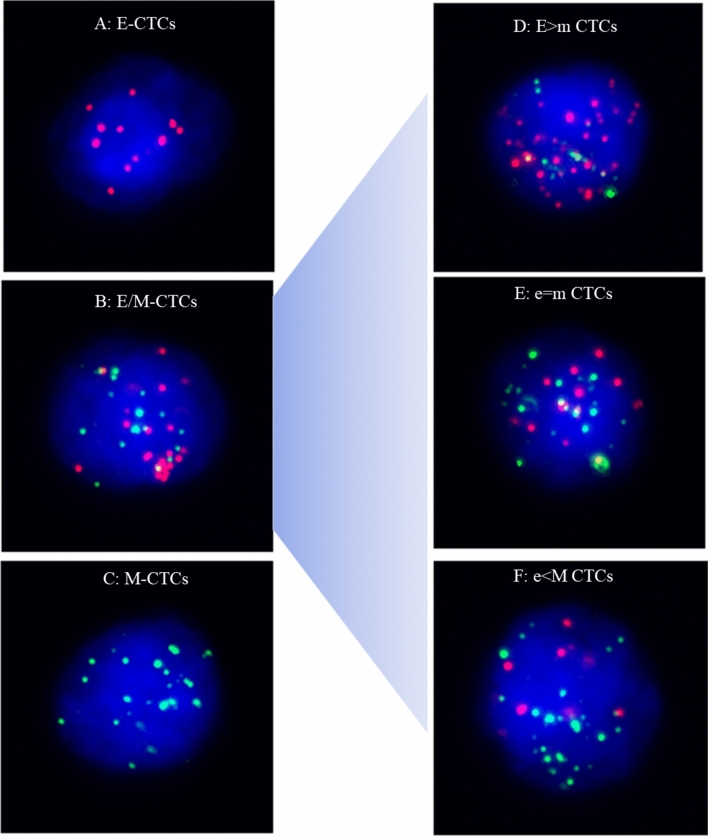
Fig. 1.
Representative images of five types of CTCs isolated from NSCLC patients based on RNA-ISH of epithelial marker(red dots) and mesenchymal marker (green dots). A E-CTCs: epithelial marker + , mesenchymal marker-, CD45–, and DAPI + cells; B: hybrid E/M-CTCs: epithelial marker + , mesenchymal marker + , CD45–, and DAPI + cells; C M-CTCs: epithelial marker-, mesenchymal marker + , CD45–, and DAPI + cells; D E > m CTCs (the fluorescence dot counts of epithelial markers were double compared to the mesenchymal markers); E e = m CTCs (the fluorescence dot counts of epithelial markers were similar to mesenchymal markers); F e < M CTCs (the fluorescence dot counts of epithelial markers were two times lower than the mesenchymal markers)