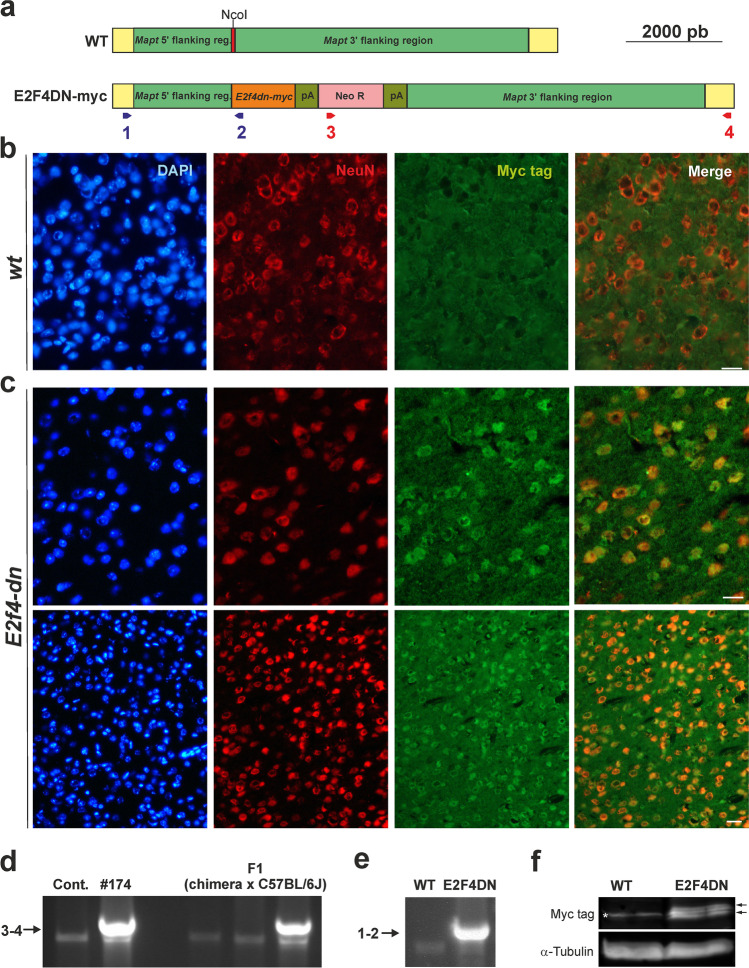
Fig. 1.
Generation and characterization of E2F4DN mice. a Scheme showing the DNA construct used to generate the E2F4DN mice. Red: Mapt Exon I containing the NcoI restriction site where the E2f4dn-myc cassette was inserted. pA: Pgk-1 polyadenylation signal, Neo R: Pgk-NeoR sequence. Primers #1 and #2, for the 5′ flanking region, are shown in blue while primers #3 and #4, for the 3′ flanking region, are depicted in red (see Methods for details). b A cerebral cortex cryosection from WT mice immunostained with anti-NeuN (red) and anti-Myc tag (green), and counterstained with DAPI. c Cerebral cortex cryosections from E2F4DN mice immunostained with anti-NeuN (red) and anti-Myc tag (green), and counterstained with DAPI. d Genomic DNA from control R1 cells (Contr.), clone #174, and three mice descendants from a cross between the founding chimera and a C57BL/6J mouse, amplified with primers #3 and #4. Arrow: band specific for the E2F4DN construct. e Genomic DNA from a WT and an E2F4DN mice, amplified with primers #1 and #2. Arrow: band specific for the E2F4DN construct. f Western blot performed with extracts from cerebral cortex of WT and E2F4DN mice using an antibody against c-Myc tag. Loading control performed with an anti α-tubulin. Asterisk: unspecific band. Arrows: specific bands. Scale bar: 20 μm (b, c upper panels), 80 μm (c bottom panels)