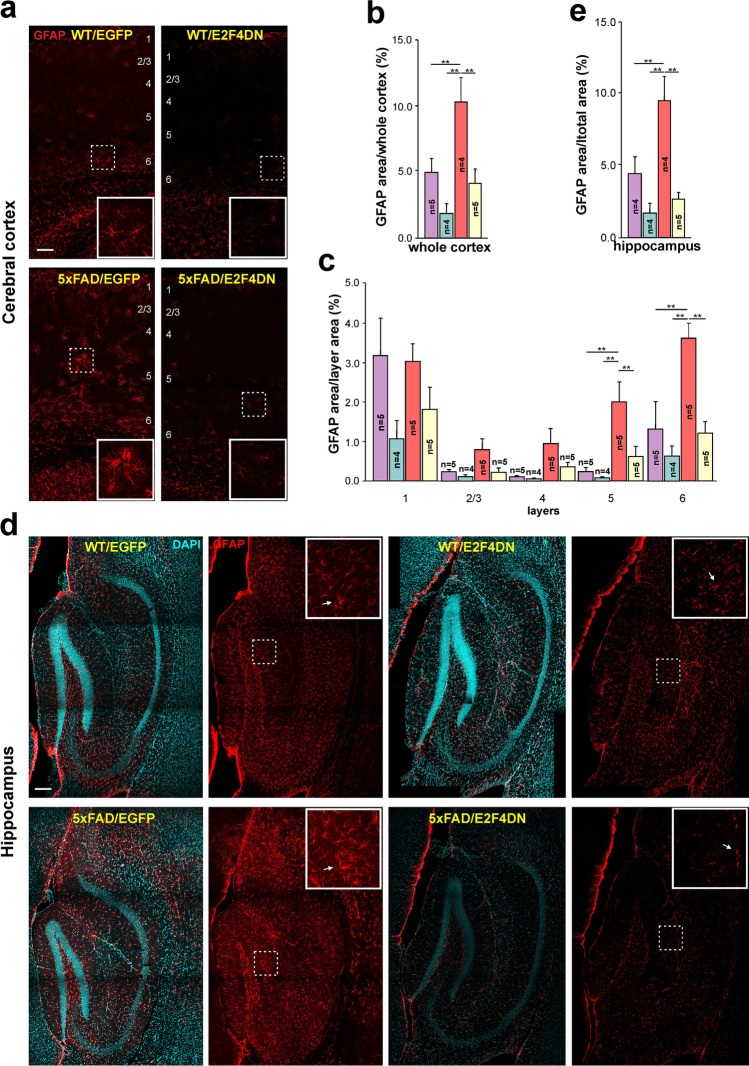
Fig. 6.
Modulation of astrogliosis by E2F4DN in cerebral cortex and hippocampus of 3 month-old 5xFAD mice. a GFAP immunostaining in the cerebral cortex of mice of the indicated genotypes. Notice the decreased GFAP-positive labeling and reactivity of astrocytes in the cerebral cortex of 5xFAD mice expressing neuronal E2F4DN. A similar trend, although not so pronounced, was also detected in WT mice expressing neuronal E2F4DN. Numbers refer to the different cortical layers. b Percentage of the area occupied by GFAP immunostaining in the cerebral cortex. c Percentages of the area occupied by GFAP immunostaining in the indicated cortical layers. d GFAP immunostaining in the hippocampus of mice of the indicated genotypes. Notice the decreased GFAP-positive labeling of astrocytes in the hippocampus of 5xFAD mice expressing neuronal E2F4DN. A similar trend, although not so pronounced, was also detected in WT mice expressing neuronal E2F4DN. e Percentage of the area occupied by GFAP immunostaining in the hippocampus. Inserts show high magnifications of the indicated dashed boxes. DAPI counterstaining is included to identify the hippocampus. **p < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Newman-Keuls test). Cortex: WT/EGFP (1 male and 4 females), WT/E2F4DN (3 males and 1 female), 5xFAD/EGFP (4 males and 1 female), and 5xFAD/E2F4DN (4 males and 1 female). Hippocampus: WT/EGFP (1 male and 3 females), WT/E2F4DN (3 males and 1 female), 5xFAD/EGFP (4 males) and 5xFAD/E2F4DN (4 males and 1 female). Scale bar: 100 μm