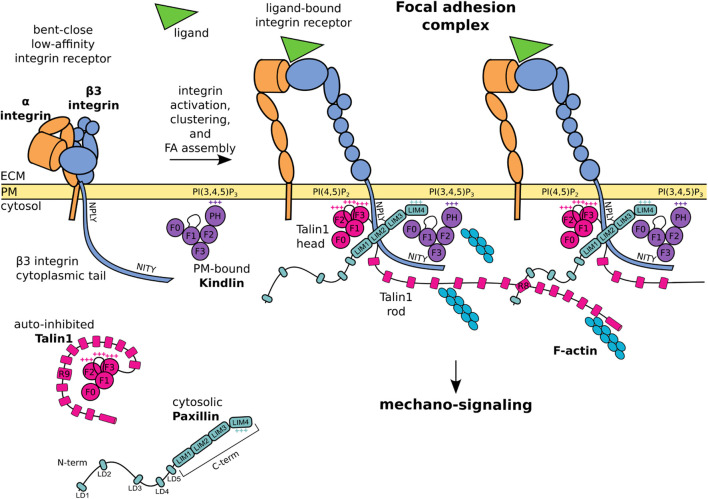
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of core FA proteins and their interactions. The β3 integrin subunit is composed of an extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain, and a C-terminal cytoplasmic tail presenting the membrane proximal NPLY talin-binding and membrane distal NITY kindlin-binding sites. The heterodimeric integrin receptor in a bent-close low-affinity conformation (left) switches to an extended-open high-affinity state and binds ligands and intracellular proteins (right). Talin1 consists of a globular head, an unstructured linker, and a C-terminal rod domain which intramolecularly interacts with the head domain to keep cytosolic talin1 auto-inhibited. Upon integrin activation, the talin1 F2 domain binds to membrane phospholipid PI(4,5)P2, the talin F3 subdomain to the membrane proximal NPLY motif in the β3 integrin cytoplasmic tail, and the talin rod engages the F-actin network. Kindlin is similarly organized to talin-head but with the addition of a PH domain inserted within the F2 domain which recognizes membrane phosphoinositides, while the F3 domain binds to the membrane-distal NITY motif in the β3 integrin cytoplasmic tail. The paxillin amino-terminal half presents five short LD motifs and is followed by the carboxyl-terminal half composed of four LIM domains. The paxillin N-terminal LD1 and LD2 interact with the talin1 R8 domain, the LIM domains point towards the membrane proximal region, the positively charged LIM4 domain interacts with kindlin and the plasma membrane. One of the paxillin LIM domain could recognize the Y presented by the NPLY motif. +++ indicates positively charged regions. For representative purposes, the β3 integrin tail is outsized and some protein domains are simplified or omitted for clarity.