FIGURE 3.
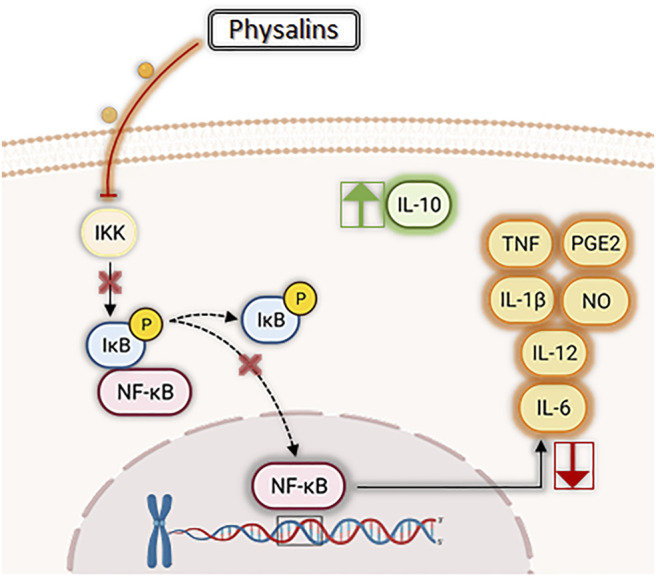
Main anti-inflammatory effects of physalins. In general, physalins suppress phosphorylation of iκB proteins and impair NF-κB translocation to the nucleus. NF-κB is involved in the regulation of several pro-inflammatory genes, and thus suppression of its activity by physalins results in inhibition of pro-inflammatory mediators, such as interleukins (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-12, nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF). In addition, some physalins (such as physalin F and H) increase the production of IL-10, a well-known anti-inflammatory cytokine.
