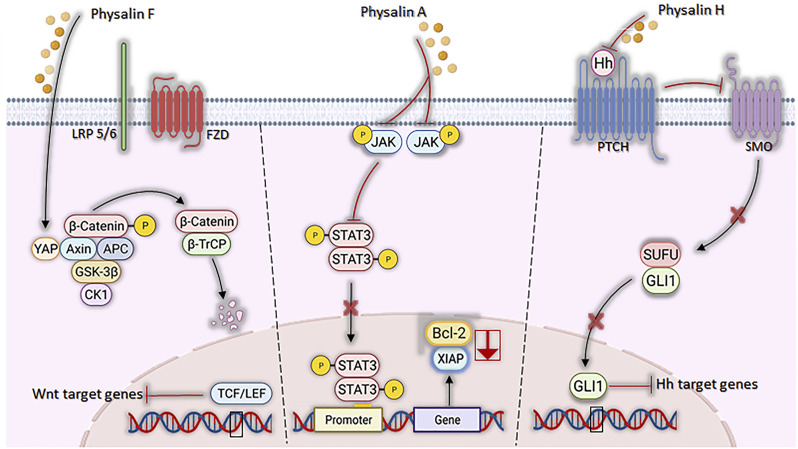
FIGURE 5.
Mechanisms of action of physalins A, F, and H in aberrant signaling pathways. Physalin F inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling, accelerating the degradation of β-catenin and promoting the binding of YAP to the Axin, APC, CK1 and GSK-3β destruction complex. β-catenin phosphorylation facilitates its recognition by β-TrCP, leading to its degradation by the ubiquitin-dependent proteasome pathway. Physalin A inhibits the phosphorylation of the JAK receptor and the STAT3 protein, inhibiting their translocation to the nucleus and downstream Bcl-2 and XIAP transcription. Physalin H inhibits the Hedgehog pathway by suppressing Hh protein expression, impeding its binding to Hh-related proteins (PTCH) and inhibiting smoothened (SMO), which in turn allows the SUFU-containing GLI processing complex to generate transcriptional repressors, disrupting binding of GLI1 to its DNA binding domain and the non-expression of PTCH and Bcl-2.