Fig. 2. Diverse cellular molecules can be targeted by RNA therapy.
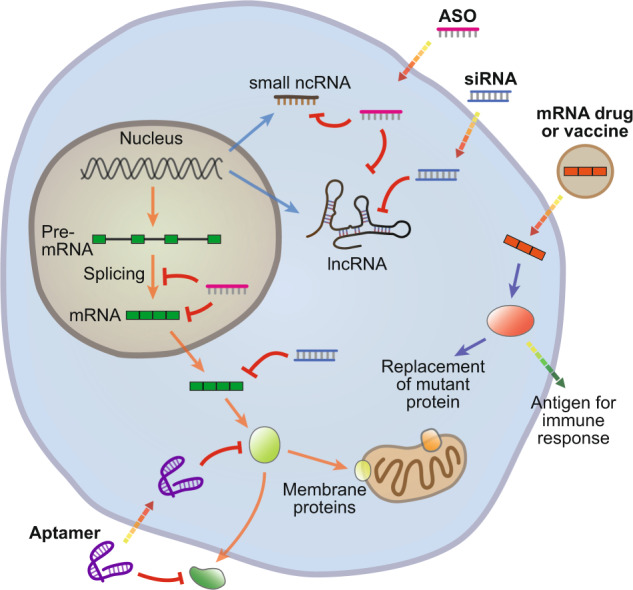
RNA-based drugs can target various steps involved in the expression of both protein-coding and noncoding genes. Splicing can be modulated by antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), and mature messenger RNAs (mRNAs) can be targeted by ASOs or small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). In addition, noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs), including small ncRNAs and long ncRNAs (lncRNAs), can be suppressed by ASOs or siRNAs. Protein function can be modulated by aptamer binding. Finally, exogenous mRNAs can be used to introduce specific proteins into cells to replenish a deficient enzyme or act as antigens to elicit a targeted immune response.
