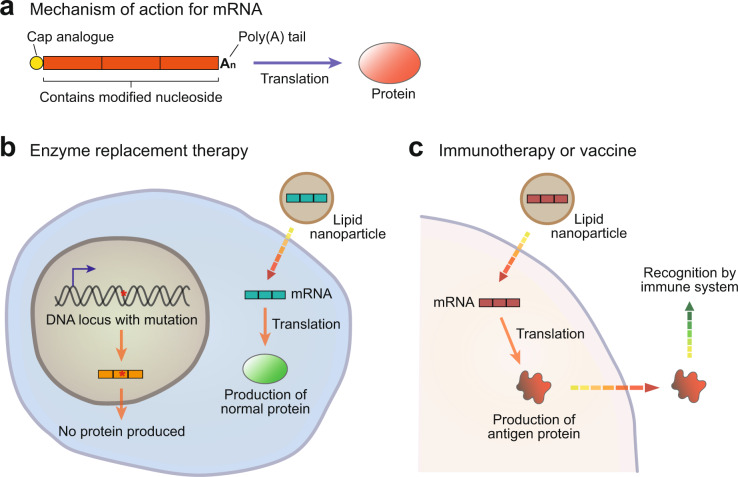
Fig. 6. Therapeutic applications of messenger RNA (mRNA).
a The mechanism of action of mRNA-based drugs. Exogenous mRNAs introduced into cells undergo translation to proteins and facilitate protein function. These mRNA constructs include a 5ʹ cap analog to facilitate their recognition by translation initiation factors, which is the first step in translation. In addition, mRNA sequences can be modified to allow evasion of the immune system, allowing them to exert their therapeutic effect for a longer period. b The use of mRNAs for enzyme replacement therapy. mRNAs are introduced into cells where the corresponding proteins are not produced due to mutation. c The use of mRNAs as vaccines. The introduced mRNAs produce proteins that may be recognized by the immune system as antigens.