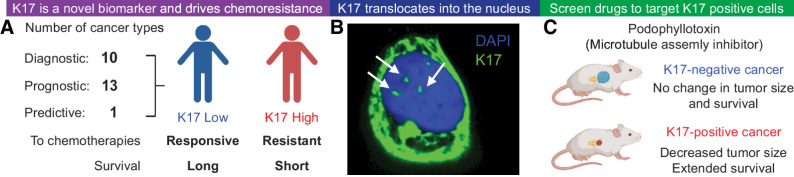
Figure 1.
Significant findings on K17 suggest it is an ideal therapeutic target. A, Overall, K17 is a predictive, prognostic, and diagnostic biomarker in several different cancers. K17 was previously found to predict therapeutic response of tumors, such that low K17 expression in tumors is correlated with longer patient survival and high K17 expression in tumors is correlated with shorter survival in patients. K17 was shown to promote chemoresistance to first-line chemotherapeutic regimens that do not target K17. B, K17 translocates into the nuclei of cancer cells to promote tumorigenic functions. Confocal imaging shows K17 (green) and nucleus staining with DAPI (blue). C, An unbiased high-throughput drug screen revealed several potential molecules that can target K17-expressing PDAC cells, including podophyllotoxin, a microtubule assembly inhibitor.