Figure 2.
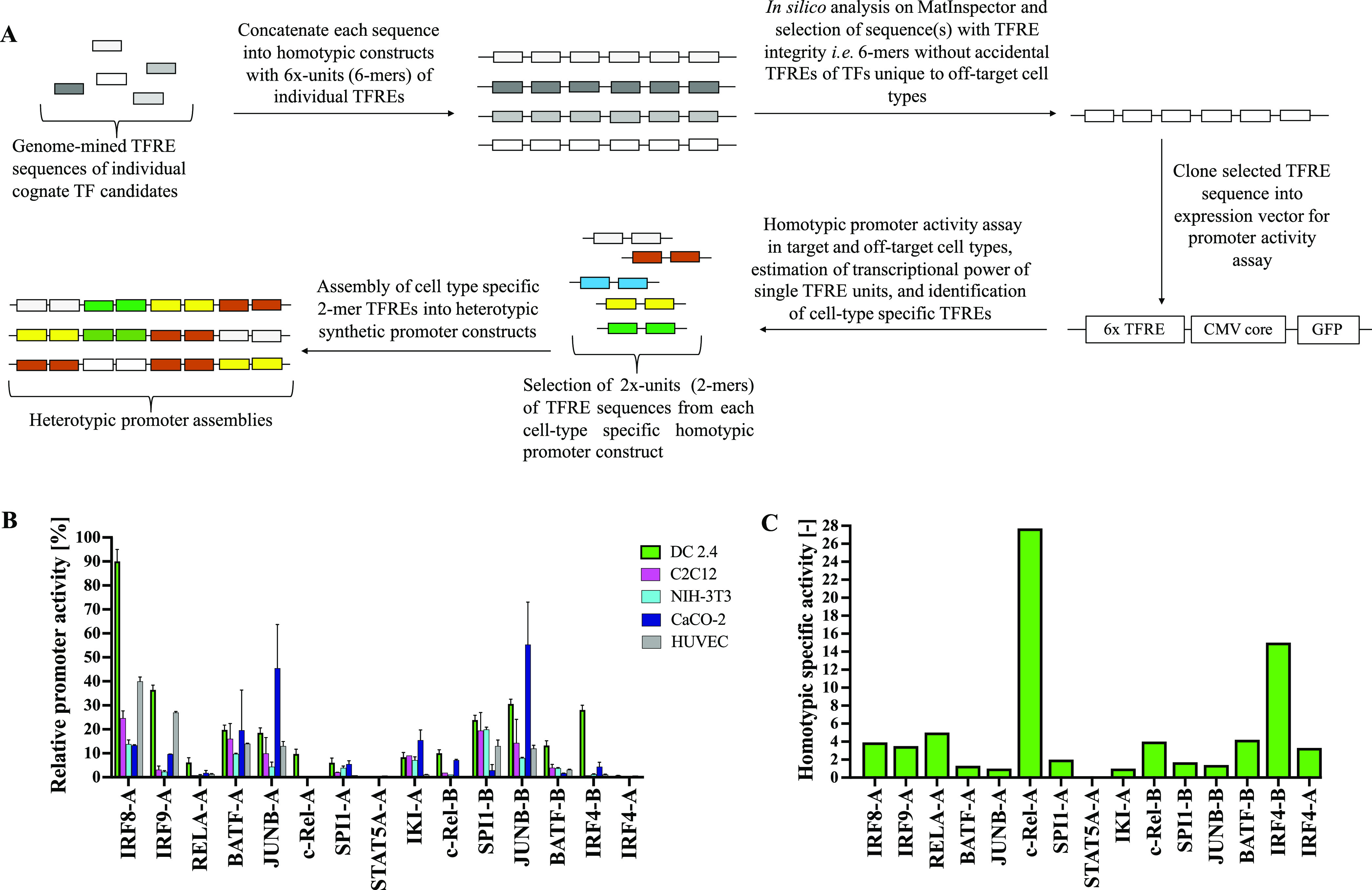
In vitro construction and screening of homotypic constructs of TFREs with respect to cell-type specificity and bioactivity for heterotypic synthetic promoter assembly. (A) Candidate TFREs derived from an informatics workflow are concatenated into 6-repeat homotypic promoter constructs which are screened for sequence composition on MatInspector. Homotypic assemblies, which do not contain undesired accidental sequences at TFRE–TFRE junctions, are selected and cloned into a GFP-reporter vector possessing the hCMV-IE1 core promoter element upstream of the CDS of the GFP, which are screened in vitro in the target (DC 2.4) and off-target cell types (C2C12, NIH-3T3, CaCO-2, HUVEC). The transcriptional power of single TFRE units is estimated, and cell-type-specific TFREs are identified. 2×-repeat elements (2-mer) of each cell-type-specific TFRE are taken from the homotypic constructs and assembled in varying ratios into heterotypic promoter constructs. (B) Relative promoter activity (RPU) of homotypic (6-mer) constructs of selected TFREs when screened for GFP expression relative to the human cytomegalovirus IE1 (hCMV-IE1) promoter (positive control) in target DC 2.4 cells and all four off-target cells. Values represent the mean ± standard deviation across three independent transfections, each performed in triplicate. (C) Homotypic promoter SS is calculated as a ratio of the RPU in DC2.4 cells and the mean RPU in all four off-target cells.
