Figure 1.
Active site of SARS-CoV-2 RdRp makes it an efficient polymerase
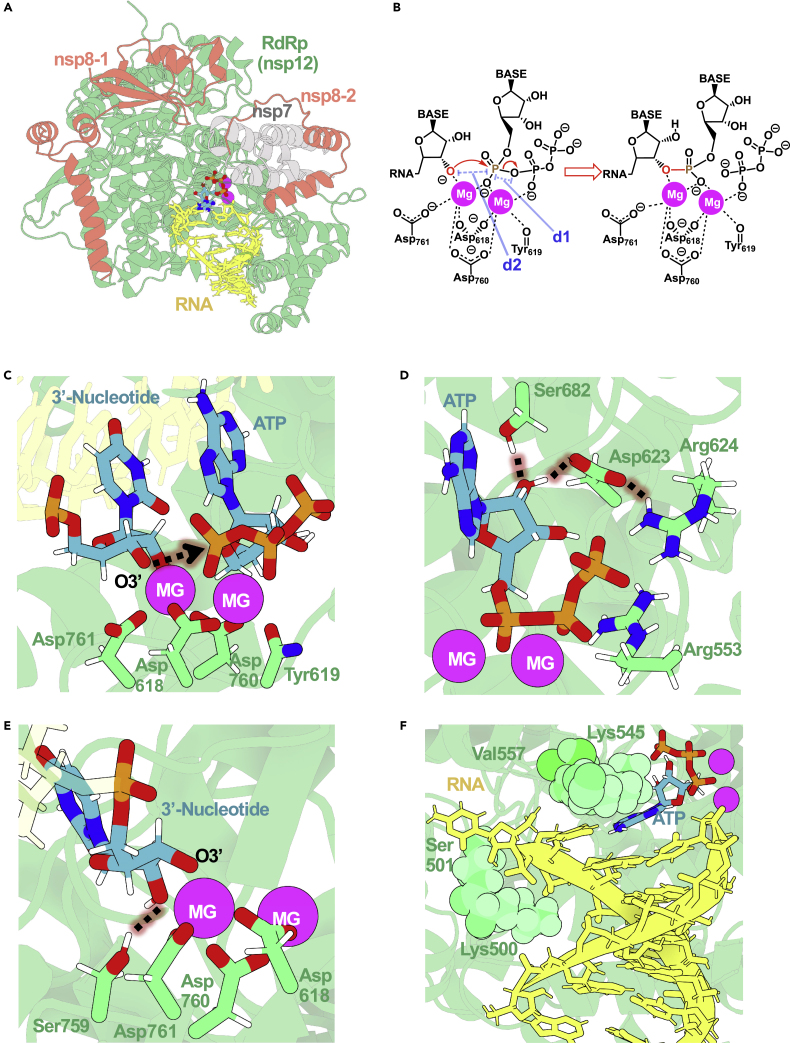
(A) The replication complex of SARS-CoV-2 formed by the nsp12 RdRp enzyme (in green), the nsp8 and nsp7 cofactors (orange and gray, respectively), and an RNA template and nascent strands (yellow).
(B) Scheme depicting the two-metal-ion mechanism used by SARS-CoV-2 RdRp.
(C) The active site contains a well-defined coordination sphere of the two Mg2+ ions.
(D) NTP substrate recognition in the active site of RdRp is mediated by a pair of arginines, an aspartate, and a serine.
(E) The deprotonated 3′ terminal nucleotide is stabilized by one of the catalytic ions in the RdRp’s active site.
(F) RdRp active site pocket enables base specificity between the incoming nucleotide and the template.
Figures were prepared with 3D Protein Imager.24 A 3D structure representation can be accessed through https://mmb.irbbarcelona.org/3dRS/s/Y17cub.