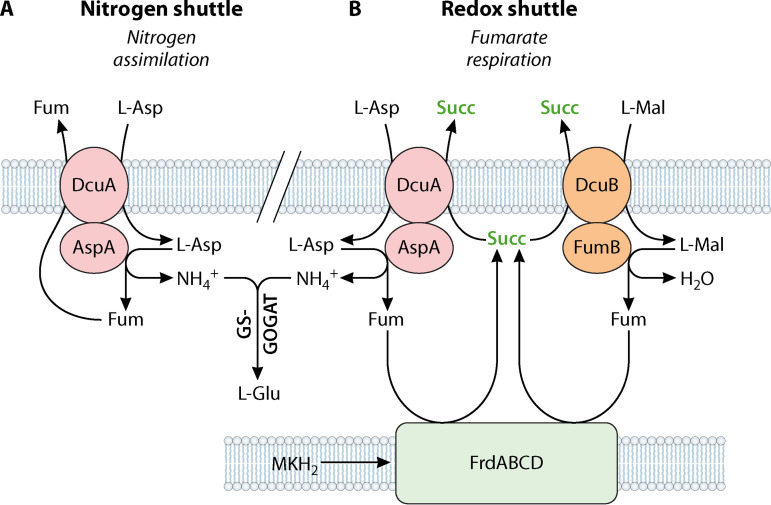
FIG 2.
Scheme for the DcuA/AspA, DcuB/AspA, and DcuB/FumB metabolons of E. coli. Complex formation between AspA and FumB with the Dcu transporters is based on interaction studies (43), suggesting metabolon formation and metabolic channeling. The l-aspartate/fumarate antiport used during nitrogen assimilation by DcuA results in net uptake of ammonium (“nitrogen or ammonium shuttle”), the fumarate/succinate or l-malate/succinate antiport in the net uptake of 2 [H] (“H or redox shuttle”) for the sake of fumarate respiration. Figure modified from Schubert and Unden (43). AspA, aspartase; DcuA, C4-DC transporter; DcuB, C4-DC transporter; FrdABCD, fumarate reductase; GS-GOGAT, glutamine synthetase (GS)-glutamine 2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase (GOGAT) pathway; Fum, fumarate; FumB, fumarase B; L-Asp, l-aspartate; L-Mal, l-malate; MKH2, menaquinol; Succ, succinate.