Figure 7.
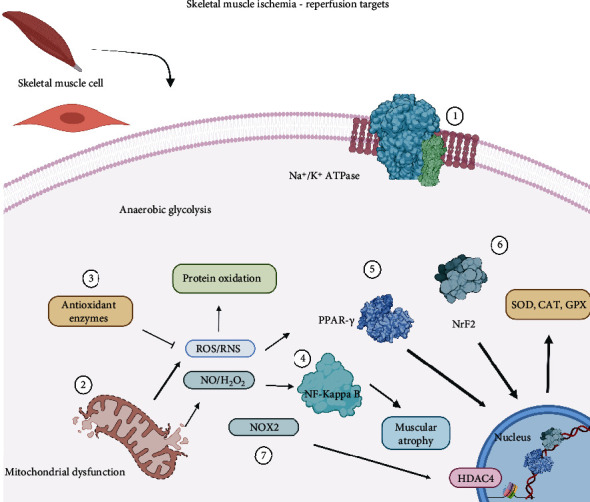
Skeletal muscle I-R targets. (1) Na+/K+ ATPase activation promotes the saturation on Na+ and K+. That is why modulation of these enzymes could be an excellent alternative to reduce damage. (2) Blocking mitochondrial release of ROS and RNS during dysfunction could improve cellular damage. (3) Scavenger activity of antioxidant enzymes is one of the main alternatives to modulate this condition. (4) Activation NF-κB leads to muscular atrophy for several inflammatory mechanisms. (5) PPAR-γ translocations, as well as NrF2 (6), result in the expression of the antioxidant complex. (7) NOX2-depending pathways conduce to activation of HDAC4 that facilitates gene expression.
