Figure 3.
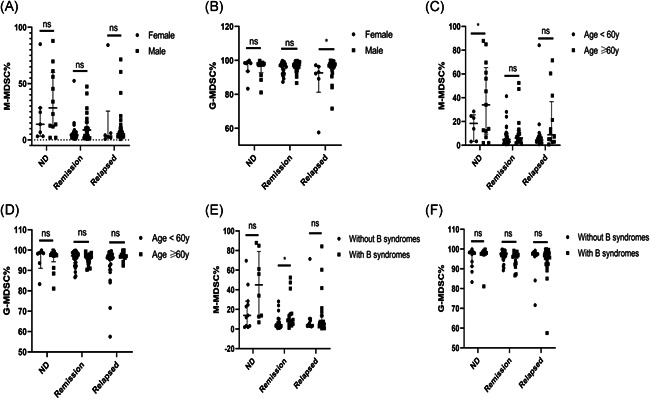
Clinical correlation of the M‐MDSCs and G‐MDSCs levels in different status of B‐NHL patients. (A) No significant difference was detected in M‐MDSC% between female and male groups in ND, remission and relapsed patients. (B) A significant difference was detected in G‐MDSC% between female and male groups in relapsed patients, and there existed no significant difference in ND and remission patients. (C) A significant difference was detected in M‐MDSC% between age <60 y and age ≥60 y groups in ND patients, and no significant difference was found in remission and relapsed patients. (D) No significant difference was detected in G‐MDSC% between age <60 y and age ≥60 y groups in ND, remission, and relapsed patients. (E) A significant difference was detected in M‐MDSCs levels between yes and no groups (Yes, with B syndromes; No, without B syndromes) of remission patients, while no significant difference was detected in ND and relapsed patients. (F) No significant difference was detected in G‐MDSCs between yes and no groups in ND, remission and relapsed patients. Each point represents an individual. *p < .05, ns p ≥ .05. B‐NHL, B‐cell non‐Hodgkin lymphoma; G‐MDSCs, granulocytic‐myeloid‐derived suppressor cells; M‐MDSCs, monocytic‐MDSC; ND, newly diagnosed
