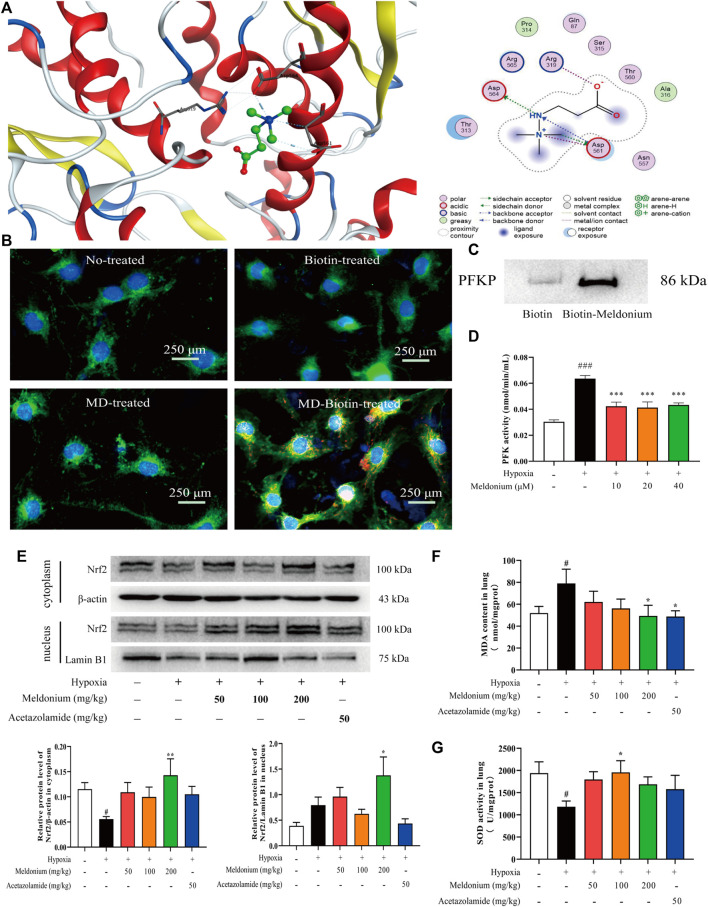
FIGURE 4.
PFKP is the potential target protein of meldonium and meldonium treatment attenuated oxidative stress induced by hypoxia. (A) Position of meldonium binding to PFKP and 2D structure diagram of meldonium interacting with PFKP. (B) Co-localisation of meldonium with PFKP in vitro. PFKP is shown in green, biotin-meldonium is shown in red, and co-localisation is shown in yellow orange. MD: meldonium. (C) Pull-down assay of meldonium-PFKP interaction in vitro was confirmed via western blot. (D) Effect of meldonium on PFK activity under hypoxia condition in vitro (n = 3). (E) Protein expression of Nrf2 in the cytoplasm and nucleus after hypoxia for 24 h in vivo (n = 6). (F) Malondialdehyde content after hypoxia for 24 h in vivo (n = 6). (G) Superoxide dismutase activity after hypoxia for 24 h in vivo (n = 6–7). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD test. #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001 compared with the control group; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared with the hypoxia group.