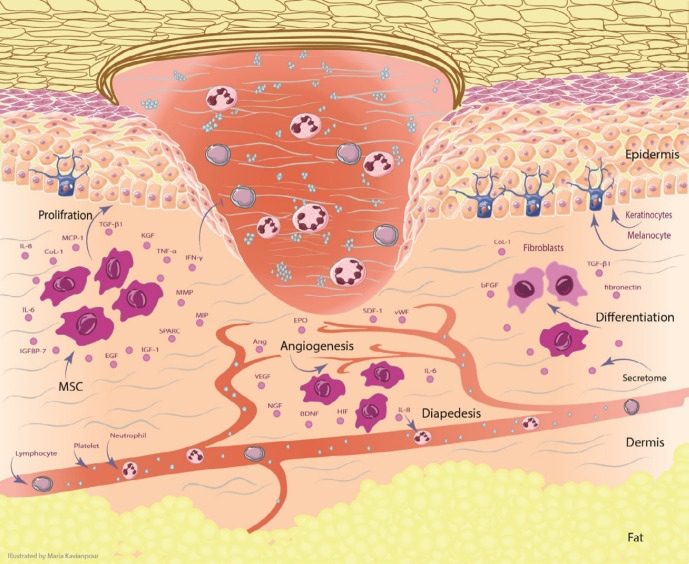
Figure 1.
The effect of MSCs and their secretome in the skin for DFU treatment. MSCs can migrate and increase angiogenesis through secreting VEGF, NGF, BDNF, Ang, SDF-1, vWF, EPO and HIF. the proliferation of keratinocytes plays the significant role in re-epithelialization. Keratinocyte function is improved by regulating IGF-1, EGF, MMP, TGF-β, KGF, MCP-1, and TIMP. MSCs can differentiate into fibroblasts by producing of Col-1, TGF-β, fibronectin, and bFGF. All of these processes can promote the wound healing in DFU. Abbreviation: Ang: angiopoietin, BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor, bFGF: basic fibroblast growth factor, Col-1: collagen type 1, DFU: Diabetic foot ulcer, EGF: epidermal growth factor, EPO: erythropoietin, HIF: hypoxia-inducible factor, IGF-1: insulin-like growth factor-1, IL: interleukin, IGFBP-7: insulin-like growth factor binding protein-7, IFN-γ: interferon-γ, KGF: keratinocyte growth factor, MMP: matrix metalloproteinase, MIP: macrophage inflammatory protein, MCP-1: monocyte chemotactic protein-1, MSCs: mesenchymal stem cells, NGF: Nerve growth factor, PGE2: Prostaglandin E2, SDF-1: stromal cell-derived factor-1, SPARC: secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine, TGF-β: transforming growth factor, TIMP: tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase, TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α, VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor, vWF: Von Willebrand factor