Fig. 4.
Cav-1 Binds to Mfn2 and Drp1.
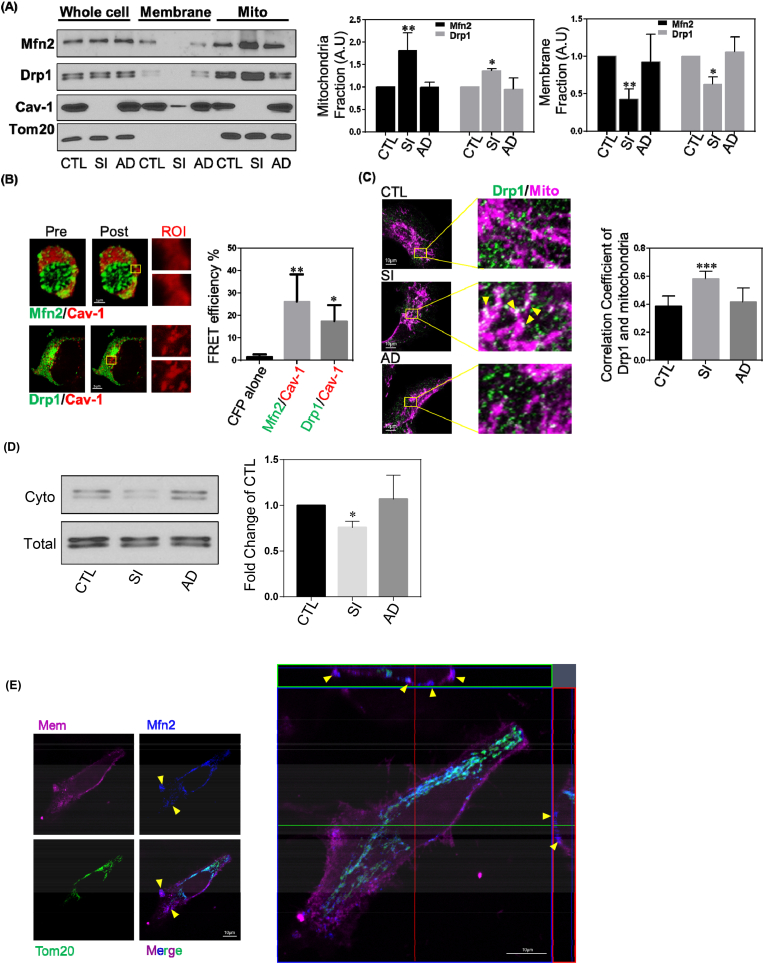
(A) Representative images of Western blots of MDA-MB-231 cells treated with Cav-1 siRNA with of without rescue with Cav-1 adenovirus. Membrane and mitochondria fractions were isolated and relative band intensities (densitometry) were determined by ImageJ. Bar graph depicts fold-change in Mfn2 and Drp1 levels in the whole cell lysates, membrane and mitochondrial fractions. Without a change in whole cell expression, Cav-1 depletion increased Mfn2 and Drp1 levels in the mitochondrial fraction. Data are mean ± SEM, n ≥ 3; **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 vs control by ANOVA.
(B) HEK cells co-transfected with Cav-1-CFP and Mfn2-YFP or Drp1-YFP were fixed and imaged by confocal microscopy. FRET intensity was calculated from CFP signal induced by 458 nm excitation after photobleaching YFP. Representative images depicting increase in CFP intensity after photobleaching region of interest. Bar graph summary of FRET efficiency of Mfn2-YFP and Drp1-YFP with Cav-1-CFP. Data are the mean ± SEM, n = 6; **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 vs CFP alone by ANOVA.
(C) MDA-MB-231 cells treated with control or Cav-1 siRNA, with and without rescue with Cav-1 adenovirus, were fixed and immunostained for Tom20 and Drp1. Quantification of Pearson's correlation coefficient of co-localized Drp1 and mitochondria labels are from over 50 cells. Data are mean ± SEM, n ≥ 10; *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 vs control by ANOVA.
(D) Cytosolic fractions versus total cell lysates were used for Drp1 Western blot. In Cav-1 repleted cells, the cytosolic Drp1 level decreased. Data are mean ± SEM, n ≥ 3; *p < 0.05 vs control by ANOVA
(E) MDA-MB-231 cells stained with MemBrite® Fix 568 were washed and fixed with 4% PFA for 20 min at RT, and then immunostained for Mfn2 and Tom20. 35 optical sections of 0.15 μm were used to reconstruct 3D images. The yellow arrow heads represent non-mitochondrial Mfn2 colocalizing with plasma membrane fluorescent label. The orthogonal view revealed spatial correlation of Mfn2 and plasma membrane fluorescence.
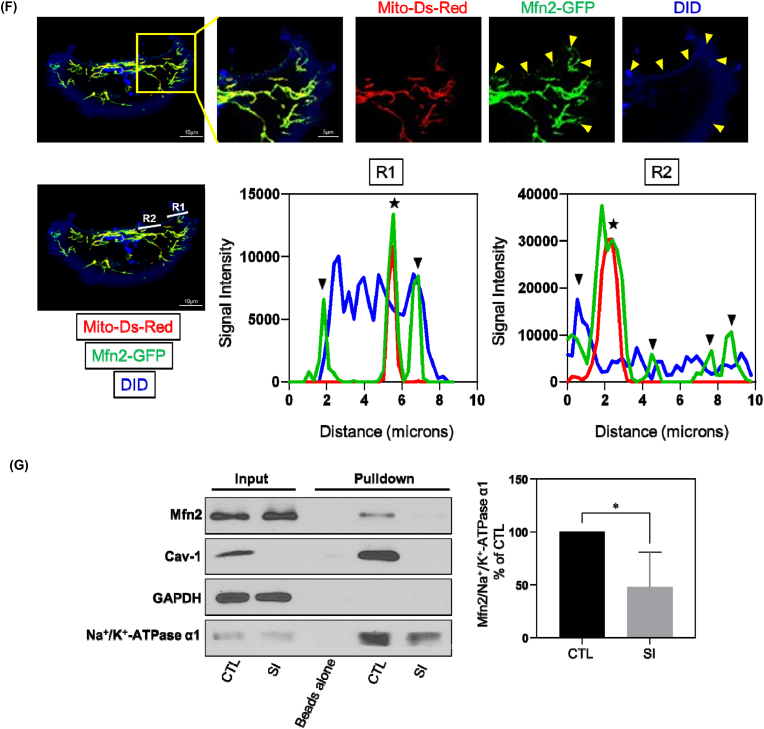
(F) MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with Mfn2-GFP and mito-Ds-Red were stained with DID and visualized by confocal microscopy. The yellow arrow heads in the representative image denote non-mitochondrial Mfn2 colocalizing with the plasma membrane. The white lines, Region1 (R1) and Region2 (R2), indicated the line scan of Mfn2-GFP, mito-Ds-Red and DID fluorescence was analyzed using ImageJ, respectively. The black arrow heads signify non-mitochondrial Mfn2-GFP colocalizing with plasma membrane and stars signify Mfn2-GFP colocalizing with mitochondria.
(G) MDA-MB-231 cells treated with control or Cav-1 siRNA were incubated with EZ-Link™ Sulfo–NHS–SS-Biotin for 45 min on ice and then lysed. The plasma membrane proteins labeled with biotin were captured by Streptavidin-coupled Dynabeads. Samples were then subjected to Western Blot analysis. GAPDH, a cytoplasmic maker, was not found in biotin surface membrane pulldown fraction suggesting there's no cytoplasmic contamination. Bar graph depicts fold-change of Mfn2 detected in biotin labeled plasma membrane fraction relative to membrane inserted Na+/K+-ATPase α1 subunit which revealed a decrease in plasma membrane-localized Mfn2 after Cav-1 depletion. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 4; *p < 0.05 vs control by Student's t-test. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)