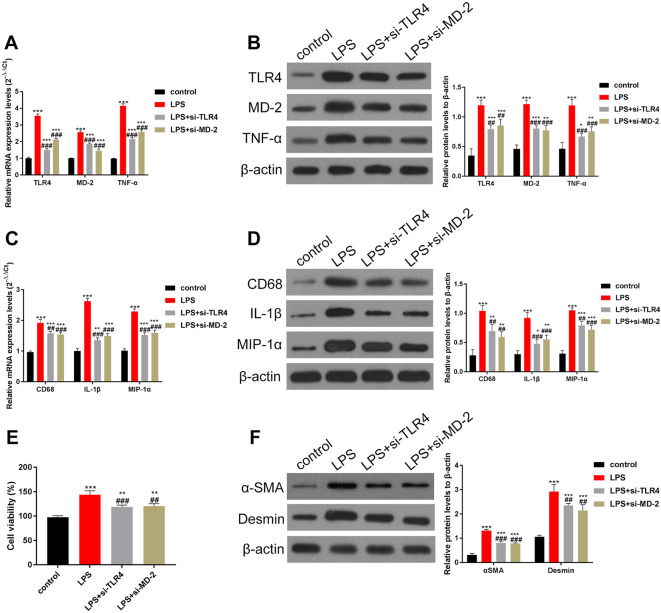
Fig. 4.
Knockdown of TLR4/MD-2 in liver KCs can partially reduce the LPS-induced activity of HSCs.
KCs and HSCs were isolated and co-cultured. Inhibition of TLR4 and MD-2 in KC cells reduced the activity of HSCs. In addition, the secretion of pro-inflammatory factors was reduced. (A–B) The expression of TLR4, MD-2, and TNF-α was determined by (A) RT-qPCR and (B) Western blotting. The increase in TLR4, MD-2, and TNF-α induced by LPS can be partially inhibited by the siRNAs of TLR4/MD-2. (C–D) The levels of CD68 and pro-inflammatory factors IL-1β and MIP-1α were detected by (C) RT-qPCR and (D) Western blotting, and data were quantified by Image J software. The expression levels of CD68, IL-1β, and MIP-1α were also partially inhibited by knocking down TLR4/MD-2. (E) The viability of HSCs was estimated using the MTT assay. (F) Expression of α-SMA and desmin, markers of HSCs, was estimated by Western blotting, and data were quantified using ImageJ software. The results indicated that the viability of HSCs was also partially inhibited by knocking down TLR4/MD-2. ***p<0.001 vs. the control group. ##p<0.01, ###p<0.001, vs. the LPS group.